BRD4 inhibitor reduces exhaustion and blocks terminal differentiation in CAR-T cells by modulating BATF and EGR1
- PMID: 39407311
- PMCID: PMC11476310
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-024-00667-w
BRD4 inhibitor reduces exhaustion and blocks terminal differentiation in CAR-T cells by modulating BATF and EGR1
Abstract
Background: Exhaustion is a key factor that influences the efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells. Our previous study demonstrated that a bromodomain protein 4 (BRD4) inhibitor can revise the phenotype and function of exhausted T cells from leukemia patients. This study aims to elucidate the mechanism by which a BRD4 inhibitor reduces CAR-T cell exhaustion using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq).
Methods: Exhausted CD123-specific CAR-T cells were prepared by co-culture with CD123 antigen-positive MV411 cells. After elimination of MV411 cells and upregulation of inhibitory receptors on the surface, exhausted CAR-T cells were treated with a BRD4 inhibitor (JQ1) for 72 h. The CAR-T cells were subsequently isolated, and scRNA-Seq was conducted to characterize phenotypic and functional changes in JQ1-treated cells.
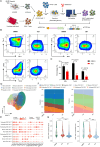
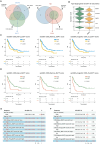
Results: Both the proportion of exhausted CD8+ CAR-T cells and the exhausted score of CAR-T cells decreased in JQ1-treated compared with control-treated cells. Moreover, JQ1 treatment led to a higher proportion of naïve, memory, and progenitor exhausted CD8+ CAR-T cells as opposed to terminal exhausted CD8+ CAR-T cells accompanied by enhanced proliferation, differentiation, and activation capacities. Additionally, with JQ1 treatment, BATF activity and expression in naïve, memory, and progenitor exhausted CD8+ CAR-T cells decreased, whereas EGR1 activity and expression increased. Interestingly, AML patients with higher EGR1 and EGR1 target gene ssGSEA scores, coupled with lower BATF and BATF target gene ssGSEA scores, had the best prognosis.
Conclusions: Our study reveals that a BRD4 inhibitor can reduce CAR-T cell exhaustion and block exhausted T cell terminal differentiation by downregulating BATF activity and expression together with upregulating EGR1 activity and expression, presenting an approach for improving the effectiveness of CAR-T cell therapy.
Keywords: BRD4 inhibitor; Chimeric antigen receptor T cell exhaustion; Single-cell RNA sequencing; Transcriptional factors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ma Y, Dai H, Cui Q, Liu S, Kang L, Lian X, et al. Decitabine in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide as a lymphodepletion regimen followed by CD19/CD22 bispecific targeted CAR T-cell therapy significantly improves survival in relapsed/refractory B-ALL patients. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023;12(1):36. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeng C. Advances in cancer treatment: the role of new technologies and research. Cell Invest. 2025;1(1):100001. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

