Nanoscale Radiotheranostics for Cancer Treatment: From Bench to Bedside
- PMID: 39407431
- PMCID: PMC11486289
- DOI: 10.1002/wnan.2006
Nanoscale Radiotheranostics for Cancer Treatment: From Bench to Bedside
Abstract
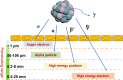
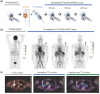
In recent years, the application of radionuclides-containing nanomaterials in cancer treatment has garnered widespread attention. The diversity of nanomaterials allows researchers to selectively combine them with appropriate radionuclides for biomedical purposes, addressing challenges faced by peptides, small molecules, or antibodies used for radionuclide labeling. However, with advantages come challenges, and nanoradionuclides still encounter significant issues during clinical translation. This review summarized the recent progress of nanosized radionuclides for cancer treatment or diagnosis. The discussion began with representative radionuclides and the methods of incorporating them into nanomaterial structures. Subsequently, new combinations of nanomaterials and radionuclides, along with their applications, were introduced to demonstrate their future trends. The benefits of nanoradionuclides included optimized pharmacokinetic properties, enhanced disease-targeting efficacy, and synergistic application with other treatment techniques. Besides, the basic rule of this section was to summarize how these nanoradionuclides can truly impact the diagnosis and therapy of various cancer types. In the last part, the focus was devoted to the nanoradionuclides currently applicable in clinics and how to address the existing issues and problems based on our knowledge.
Keywords: cancer therapy; nanoradionuclides; nuclear imaging; radiolabeling method; theranostics.
© 2024 The Author(s). WIREs Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Weibo Cai declares conflict of interest with the following corporations: Portrai, Inc., rTR Technovation Corporation, and Four Health Global Pharmaceuticals Inc.. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ancira‐Cortez, A. , Ferro‐Flores G., Jiménez‐Mancilla N., et al. 2020. “Synthesis, Chemical and Biochemical Characterization of Lu2O3‐iPSMA Nanoparticles Activated by Neutron Irradiation.” Materials Science & Engineering. C, Materials for Biological Applications 117: 111335. 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111335. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aslan, T. N. , Aşık E., and Volkan M.. 2016. “Preparation and Labeling of Surface‐Modified Magnetoferritin Protein Cages With a Rhenium(I) Carbonyl Complex for Magnetically Targeted Radiotherapy.” RSC Advances 6, no. 11: 8860–8869. 10.1039/C5RA19696E. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

