Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis: An Effective Tool to Characterize Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 39407601
- PMCID: PMC11477862
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29194672
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis: An Effective Tool to Characterize Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
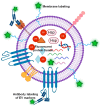
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-enclosed particles that have attracted much attention for their potential in disease diagnosis and therapy. However, the clinical translation is limited by the dosing consistency due to their heterogeneity. Among various characterization techniques, nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) offers distinct benefits for EV characterization. In this review, we will discuss the NTA technique with a focus on factors affecting the results; then, we will review the two modes of the NTA techniques along with suitable applications in specific areas of EV studies. EVs are typically characterized by their size, size distribution, concentration, protein markers, and RNA cargos. The light-scattering mode of NTA offers accurate size, size distribution, and concentration information in solution, which is useful for comparing EV isolation methods, storage conditions, and EV secretion conditions. In contrast, fluorescent mode of NTA allows differentiating EV subgroups based on specific markers. The success of fluorescence NTA heavily relies on fluorescent tags (e.g., types of dyes and labeling methods). When EVs are labeled with disease-specific markers, fluorescence NTA offers an effective tool for disease detection in biological fluids, such as saliva, blood, and serum. Finally, we will discuss the limitations and future directions of the NTA technique in EV characterization.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles; fluorescent labeling; nanoparticle-tracking analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

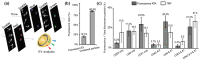
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

