Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Protocatechuic Acid in the Treatment of Cognitive Impairment
- PMID: 39407652
- PMCID: PMC11478363
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29194724
Research Progress on the Mechanisms of Protocatechuic Acid in the Treatment of Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
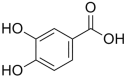
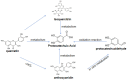
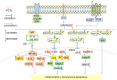
Cognitive impairment (CI) is a type of mental health disorder that mainly affects cognitive abilities, such as learning, memory, perception, and problem-solving. Currently, in clinical practice, the treatment of cognitive impairment mainly focuses on the application of cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists; however, there is no specific and effective drug yet. Procatechuic acid (PCA) possesses various functions, including antibacterial, antiasthmatic, and expectorant effects. In recent years, it has received growing attention in the cognitive domain. Therefore, by summarizing the mechanisms of action of procatechuic acid in the treatment of cognitive impairment in this paper, it is found that procatechuic acid has multiple effects, such as regulating the expression of neuroprotective factors, inhibiting cell apoptosis, promoting the autophagy-lysosome pathway, suppressing oxidative stress damage, inhibiting inflammatory responses, improving synaptic plasticity dysfunction, inhibiting Aβ deposition, reducing APP hydrolysis, enhancing the cholinergic system, and inhibiting the excitotoxicity of neuronal cells. The involved signaling pathways include activating Pi3K-akt-mTor and inhibiting JNK, P38 MAPK, P38-ERK-JNK, SIRT1, and NF-κB/p53, etc. This paper aims to present the latest progress in research on procatechuic acid, including aspects such as its chemical properties, sources, pharmacokinetics, mechanisms for treating neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; mechanism of action; procatechuic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of traditional Chinese medicine Naofucong on diabetic cognitive impairment: Mechanisms involving insulin-degrading enzyme-mediated degradation of Amyloid-β and inhibition of ERK/JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway.Brain Res. 2025 Feb 15;1849:149365. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2024.149365. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 39617284
-
Protocatechuic acid inhibits Toll-like receptor-4-dependent activation of NF-κB by suppressing activation of the Akt, mTOR, JNK and p38-MAPK.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Feb;55:272-281. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.12.024. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29291542
-
GLP-1 analogue liraglutide attenuates CIH-induced cognitive deficits by inhibiting oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 and MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;142(Pt B):113222. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113222. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39321702
-
Signaling Pathways Involved in the Neuroprotective Effect of Osthole: Evidence and Mechanisms.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Feb;61(2):1100-1118. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03580-9. Epub 2023 Sep 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37682453 Review.
-
Pre-clinical Evidence-based Neuroprotective Potential of Naringin against Alzheimer's Disease-like Pathology: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(9):1112-1123. doi: 10.2174/1389201024666230801095526. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37526460 Review.
Cited by
-
Protocatechuic Acid Attenuates Inflammation in Macrophage-like Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in ApoE-/- Mice.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 20;17(6):1090. doi: 10.3390/nu17061090. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40292571 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorating Effect of Fermented Perilla frutescens on Sleep Deprivation-Induced Cognitive Impairment Through Antioxidant and BDNF Signaling in Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 6;16(23):4224. doi: 10.3390/nu16234224. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skovgård K., Agerskov C., Kohlmeier K.A., Herrik K.F. The 5-HT3 receptor antagonist ondansetron potentiates the effects of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor donepezil on neuronal network oscillations in the rat dorsal hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 2018;143:130–142. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.09.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernal-Mercado A.T., Vazquez-Armenta F.J., Tapia-Rodriguez M.R. Comparison of Single and Combined Use of Catechin, Protocatechuic, and Vanillic Acids as Antioxidant and Antibacterial Agents against Uropathogenic Escherichia Coli at Planktonic and Biofilm Levels. Molecules. 2018;23:2813. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112813. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

