Synthesis, Physicochemical Characterization, and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Halogen-Substituted Non-Metal Pyridine Schiff Bases
- PMID: 39407654
- PMCID: PMC11477791
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29194726
Synthesis, Physicochemical Characterization, and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Halogen-Substituted Non-Metal Pyridine Schiff Bases
Abstract
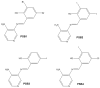
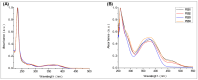
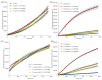
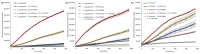
Four synthetic Schiff bases (PSB1 [(E)-2-(((4-aminopyridin-3-yl)imino)methyl)-4,6-dibromophenol], PSB2 [(E)-2-(((4-aminopyridin-3-yl)imino)methyl)-4,6-diiodophenol], PSB3 [(E)-2-(((4-aminopyridin-3-yl)imino)methyl)-4-iodophenol], and PSB4 [(E)-2-(((4-aminopyridin-3-yl)imino)methyl)-4-chloro-6-iodophenol]) were fully characterized. These compounds exhibit an intramolecular hydrogen bond between the hydroxyl group of the phenolic ring and the nitrogen of the azomethine group, contributing to their stability. Their antimicrobial activity was evaluated against various Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, and it was found that the synthetic pyridine Schiff bases, as well as their precursors, showed no discernible antimicrobial effect on Gram-negative bacteria, including Salmonella Typhi (and mutant derivatives), Salmonella Typhimurium, Escherichia coli, and Morganella morganii. In contrast, a more pronounced biocidal effect against Gram-positive bacteria was found, including Bacillus subtilis, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Among the tested compounds, PSB1 and PSB2 were identified as the most effective against Gram-positive bacteria, with PSB2 showing the most potent biocidal effects. Although the presence of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was noted after treatment with PSB2, the primary mode of action for PSB2 does not appear to involve ROS generation. This conclusion is supported by the observation that antioxidant treatment with vitamin C only partially mitigated bacterial inhibition, indicating an alternative biocidal mechanism.
Keywords: ROS; antimicrobial activity; intramolecular hydrogen bond; pyridine Schiff bases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
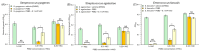
References
-
- Cui Z., Jiang P., Leng Y., Feng S., Lu M., Chen S., Sheng X. Synthesis of zinc Schiff base complex and its application as highly efficient thermal stabilizer for flexible poly (vinyl chloride) Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023;211:110317. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2023.110317. - DOI
-
- Ahmed D.S., Kadhom M., Hadi A.G., Bufaroosha M., Salih N., Al-Dahhan W.H., Yousif E. Tetra Schiff Bases as Polyvinyl Chloride Thermal Stabilizers. Chemistry. 2021;3:288–295. doi: 10.3390/chemistry3010021. - DOI
-
- Senthil Kumar R., Archana S., Archana T., Divya R., Praveen S., Shridharshini K. Synthetic approaches of medicinally important Schiff bases: An updated Review. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2022;16:838–852. doi: 10.30574/wjarr.2022.16.3.1394. - DOI
-
- Mirza-Aghayan M., Heidarian M., Alizadeh M. Pd-Isatin-Schiff base complex supported on graphene oxide as a catalyst for the Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction. J. Organomet. Chem. 2024;1009:123079. doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2024.123079. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

