Inclusion Complexation of Remdesivir with Cyclodextrins: A Comprehensive Review on Combating Coronavirus Resistance-Current State and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 39407710
- PMCID: PMC11477750
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29194782
Inclusion Complexation of Remdesivir with Cyclodextrins: A Comprehensive Review on Combating Coronavirus Resistance-Current State and Future Perspectives
Abstract
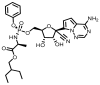
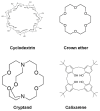
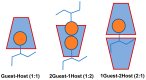
Cyclodextrin (CD) derivatives have gained significant attention in biomedical applications due to their remarkable biocompatibility, unique inclusion capabilities, and potential for functionalization. This review focuses on recent advancements in CD-based assemblies, specifically their role in improving drug delivery, emphasizing remdesivir (RMD). The review introduces CD materials and their versatile applications in self-assembly and supramolecular assembly. CD materials offer immense potential for designing drug delivery systems with enhanced activity. Their inherent inclusion capabilities enable the encapsulation of diverse therapeutic agents, including RMD, resulting in improved solubility, stability, and bioavailability. The recent advances in CD-based assemblies, focusing on their integration with RMD have been concentrated here. Various strategies for constructing these assemblies are discussed, including physical encapsulation, covalent conjugation, and surface functionalization techniques. Furthermore, exploring future directions in these fields has also been provided. Ongoing research efforts are directed toward developing novel CD derivatives with enhanced properties, such as increased encapsulation efficiency and improved release kinetics. Moreover, the integration of CD-based assemblies with advanced technologies such as nanomedicine and gene therapy holds tremendous promise for personalized medicine and precision therapeutics.
Keywords: COVID-19; cyclodextrins; inclusion complexes; remdesivir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wieslaw M.K. Antiviral Drugs: From Basic Discovery through Clinical Trials. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

