Significance as a Prognostic Factor of Eosinophil Count in Nasal Polyp Tissue in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Accompanied by Asthma
- PMID: 39407908
- PMCID: PMC11477001
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13195849
Significance as a Prognostic Factor of Eosinophil Count in Nasal Polyp Tissue in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Accompanied by Asthma
Abstract
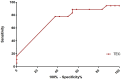
Background/Objectives: Patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) accompanied by asthma often show poor prognoses and require continuous management. This study aimed to assess the prognostic value of eosinophil counts in nasal polyp tissue for selecting individuals who would benefit from ongoing management in CRS patients with asthma. Methods: Patients with asthma who underwent endoscopic sinus surgery for CRS with nasal polyps were included in the study. Eosinophil counts in nasal polyp tissues were quantified, and retrospective data were collected from laboratory and clinical findings, including endoscopic examinations, CT scans, and Japan Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Rating and Evaluation Committee (JESREC) scores. Disease control status was evaluated through endoscopic examination 6 months post-surgery. Results: A total of 42 patients were divided into two groups based on their disease management status 6 months post-operation: the well-control group (24 patients, 57.14%) and the poor-control group (18 patients, 42.86%). Demographics and laboratory findings did not show significant differences between the groups. However, the JESREC score (p = 0.04) and tissue eosinophil count (p = 0.02) were significantly different. Multivariate analysis identified tissue eosinophil count as the only risk factor associated with prognosis, with a cut-off value of 90/HPF. Conclusions: In CRS patients with asthma, high tissue eosinophil counts in nasal polyps were associated with poor disease control, which is the most potent predictor of prognosis. The assessment of eosinophil counts in nasal polyp tissue could aid in identifying patients who would benefit from continuous management and tailored interventions for improved outcomes.
Keywords: asthma; eosinophil; rhinosinusitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mygind N. Nasal Allergy. Blackwell Scientific Publications; Oxford, UK: 1978.
-
- Tomassen P., Vandeplas G., Van Zele T., Cardell L.O., Arebro J., Olze H., Förster-Ruhrmann U., Kowalski M.L., Olszewska-Ziąber A., Holtappels G., et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016;137:1449–1456. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.12.1324. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vlaminck S., Vauterin T., Hellings P.W., Jorissen M., Acke F., Van Cauwenberge P., Bachert C., Gevaert P. The importance of local eosinophilia in the surgical outcome of chronic rhinosinusitis: A 3-year prospective observational study. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy. 2014;28:260–264. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2014.28.4024. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources