SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Coverage in Italian Children with Celiac Disease
- PMID: 39407910
- PMCID: PMC11477183
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13195851
SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Coverage in Italian Children with Celiac Disease
Abstract
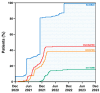
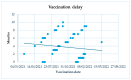
Background: Celiac disease (CD) is the most common multisystemic autoimmune disorder affecting the pediatric population. However, little data is available regarding SARS-CoV-2 vaccination coverage in pediatric patients with CD. This study aims to evaluate the adherence to national recommendations for SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in children and adolescents with CD and its variation over time. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed medical charts and electronic registry records of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination of patients aged 0-19 years diagnosed with CD in a tertiary center. The vaccination coverage was evaluated according to age groups (young children, children, and adolescents), considering the patients' eligibility for vaccination at different times. Results: Among the 172 patients enrolled, 44.8% received at least one dose of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, showing no significant differences compared to the Italian population of similar age. Vaccination coverage demonstrated a progressive reduction after an initial peak (up to 65.5% in December 2021) concomitant with a gradual extension of vaccinable eligibility and falling SARS-CoV-2 infections. Histological diagnosis and the presence of other associated autoimmune diseases were associated with higher levels of adherence to vaccination. Conclusions: Adherence to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in young Italian children with CD was very low, while it was better in adolescents and patients with other associated autoimmune diseases. Vaccine hesitancy remains a concern, particularly among those diagnosed using the biopsy-sparing approach. Hesitancy increased during the pandemic period, suggesting the need for ongoing efforts to improve adherence to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination recommendations.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; autoimmunity; celiac disease; gluten; vaccination; vaccine hesitancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Crocco M., Malerba F., Calvi A., Zampatti N., Gandullia P., Madeo A., Tappino B., Proietti S., Bonassi S. Health-related quality of life in children with coeliac disease and in their families: A long-term follow-up study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2024;78:105–112. doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12049. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous