Leukocyte Indices as Markers of Inflammation and Predictors of Outcome in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 39407935
- PMCID: PMC11477419
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13195875
Leukocyte Indices as Markers of Inflammation and Predictors of Outcome in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract
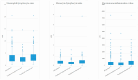
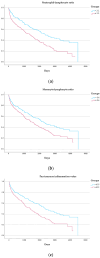
Background: The pathophysiology of heart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is suggested to be influenced by inflammation. Leukocyte indices, including the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (MLR), and the pan-immune inflammation value (PIV), can be utilized as biomarkers of systemic inflammation. Their prognostic utility is yet to be fully understood. Methods: Between December 2010 and May 2023, patients presenting to a tertiary referral center for HFpEF were included into a prospective registry. The association of the NLR, MLR, and PIV with the composite endpoint of all-cause mortality and HF-related hospitalization was tested utilizing Cox regression analysis. Results: In total, 479 patients (median 74.3, interquartile range (IQR): 69.22-78.3 years, 27.8% male) were included. Patients were observed for 43 (IQR: 11-70) months, during which a total of 267 (55.7%) patients met the primary endpoint. In a univariate Cox regression analysis, an above-the-median NLR implied a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.76 (95%-confidence interval (CI): 1.38-2.24, p < 0.001), an MLR of 1.46 (95%-CI: 1.14-1.86, p = 0.003), and a PIV of 1.67, 95%-CI: 1.30-2.13, p < 0.001) for the composite endpoint. After adjustment in a step-wise model, the NLR (HR: 1.81, 95%-CI: 1.22-2.69, p = 0.003), the MLR (HR: 1.57, 95%-CI: 1.06-2.34, p = 0.026), and the PIV (HR: 1.64, 95%-CI: 1.10-2.46, p = 0.015) remained significantly associated with the combined endpoint. Conclusions: The NLR, the MLR, and the PIV are simple biomarkers independently associated with outcomes in patients with HFpEF.
Keywords: heart failure with preserved ejection fraction; leukocyte indices; systemic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
C.H. has received payments for proctoring from Edwards and Boston Scientific, travel grants from Edwards, Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, is a member of a clinical event committee for Highlife and of a steering committee for Envisage and Daiichi Sankyo. All other others declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sanders-Van Wijk S., Tromp J., Beussink-Nelson L., Hage C., Svedlund S., Saraste A., Swat S.A., Sanchez C., Njoroge J., Tan R.S., et al. Proteomic Evaluation of the Comorbidity-Inflammation Paradigm in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Results from the PROMIS-HFpEF Study. Circulation. 2020;142:2029–2044. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.045810. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Regan J.A., Truby L.K., Tahir U.A., Katz D.H., Nguyen M., Kwee L.C., Deng S., Wilson J.G., Mentz R.J., Kraus W.E., et al. Protein Biomarkers of Cardiac Remodeling and Inflammation Associated with HFpEF and Incident Events. Sci. Rep. 2022;12:20072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24226-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Curran F.M., Bhalraam U., Mohan M., Singh J.S., Anker S.D., Dickstein K., Doney A.S., Filippatos G., George J., Metra M., et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio and Outcomes in Patients with New-onset or Worsening Heart Failure with Reduced and Preserved Ejection Fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 2021;8:3168. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13424. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

