Extraperitoneal Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy with the Hugo™ RAS System: Initial Experience at a High-Volume Robotic Centre
- PMID: 39407976
- PMCID: PMC11477504
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13195916
Extraperitoneal Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy with the Hugo™ RAS System: Initial Experience at a High-Volume Robotic Centre
Abstract
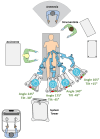
Background: The Hugo™ Robotic-Assisted Surgery (Hugo™ RAS) system represents a novel advancement in robotic surgical technology. Despite this, there remains a scarcity of data regarding extraperitoneal robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (eRARP) using this system. Methods: We conducted a prospective study at Ospedale Regionale "F. Miulli" from June 2023 to January 2024, enrolling consecutive patients diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa) undergoing eRARP ± lymph node dissection. All procedures employed a modular four-arm setup performed by two young surgeons with limited prior robotic surgery experience. This study aims to evaluate the safety and feasibility of eRARP using the Hugo™ RAS system, reporting comprehensive preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative outcomes in the largest reported cohort to date. Results: A total of 50 cases were analyzed, with a mean patient age of 65.76 (±5.57) years. The median operative time was 275 min (Q1-Q3 150-345), and the console time was 240 min (Q1-Q3 150-300). The docking time averaged 10 min (Q1-Q3 6-20). There were no intraoperative complications recorded. Two major complications occurred within the first 90 days. At the 3-month mark, 36 patients (72%) achieved undetectable PSA levels (<0.1 ng/mL). Social continence was achieved by 66% of patients, while 40% maintained erectile function. Conclusions: eRARP utilizing the Hugo™ RAS system demonstrated effectiveness and safety in our study cohort. However, more extensive studies with larger cohorts and longer follow-up periods are necessary to thoroughly evaluate long-term outcomes.
Keywords: Medtronic Hugo RAS system; new robotic platform; prostate cancer; robot-assisted radical prostatectomy; robotic surgery; surgical outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Moschovas M.C., Jaber A., Saikali S., Sandri M., Bhat S., Rogers T., Gamal A., Loy D., Patel E., Reddy S., et al. Impacts on functional and oncological outcomes of Robotic-assisted Radical Prostatectomy 10 years after the US Preventive Service Taskforce recommendations against PSA screening. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2024;50:65–79. doi: 10.1590/s1677-5538.ibju.2023.0530. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walz J., Epstein J.I., Ganzer R., Graefen M., Guazzoni G., Kaouk J., Menon M., Mottrie A., Myers R.P., Patel V., et al. A Critical Analysis of the Current Knowledge of Surgical Anatomy of the Prostate Related to Optimisation of Cancer Control and Preservation of Continence and Erection in Candidates for Radical Prostatectomy: An Update. Eur. Urol. 2016;70:301–311. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.01.026. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous