Comparative Analysis of Verapamil Pharmacokinetics: Evaluating the Impact of Simple Suspension and Crushing Administration Methods
- PMID: 39408029
- PMCID: PMC11477534
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13195969
Comparative Analysis of Verapamil Pharmacokinetics: Evaluating the Impact of Simple Suspension and Crushing Administration Methods
Abstract
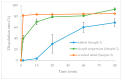
Background/Objective: It is not uncommon for elderly patients to experience difficulties with feeding and swallowing. In the simple suspension method, tablets are dissolved and suspended in warm water without prior crushing or decapsulation, and then administered via a tube. Despite the prevalence of this method, the pharmacokinetics of suspended tablet dosage forms remain poorly understood. Methods: Verapamil was employed in dissolution tests following both the simple suspension and crushing methods. A pharmacokinetics study was conducted on healthy adult males. Results: The resultant dissolution profiles from the two methods exhibited notable dissimilarities. Drug release from the crushed product commenced earlier than that from the simple suspension and intact tablet. Furthermore, the area under the curve for verapamil during the initial 24 h period was 1.7 and 1.3 times greater in the crushed and simple suspension groups, respectively, than in the tablet group. Conclusions: The crushing and simple suspension methods are safe techniques for administering medications to patients with dysphagia, thereby preventing aspiration. Nevertheless, the processing of medications may result in an increased frequency of adverse effects. It is recommended that the processing of medicines prior to administration be avoided.
Keywords: oral administration; pharmacokinetics; simple suspension method; tablet crushing; verapamil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crushed Tablet Administration for Patients with Dysphagia and Enteral Feeding: Challenges and Considerations.Drugs Aging. 2023 Oct;40(10):895-907. doi: 10.1007/s40266-023-01056-y. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Drugs Aging. 2023. PMID: 37707775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of in vitro dissolution profiles of modified-release metoprolol succinate tablets crushed using mortar and pestle technique.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024 Mar 1;194:106694. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2024.106694. Epub 2024 Jan 7. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38191064
-
Evaluation of crushed ticagrelor tablet doses: recovery following crushing and naso-gastric tube passage ex vivo.Drugs R D. 2013 Jun;13(2):153-7. doi: 10.1007/s40268-013-0018-4. Drugs R D. 2013. PMID: 23737454 Free PMC article.
-
Crushing of dolutegravir fixed-dose combination tablets increases dolutegravir exposure.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018 Sep 1;73(9):2430-2434. doi: 10.1093/jac/dky191. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29796595 Clinical Trial.
-
Paediatric formulations of artemisinin-based combination therapies for treating uncomplicated malaria in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 8;12(12):CD009568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009568.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33289099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Annual Health, Labour and Welfare Report 2022. [(accessed on 7 March 2023)]. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/wp/hakusyo/kousei/21/dl/zentai.pdf.
-
- Sugiyama M., Takada K., Shinde M., Matsumoto N., Tanaka K., Kiriya Y., Nishimoto E., Kuzuya M. National survey of the prevalence of swallowing difficulty and tube feeding use as well as implementation of swallowing evaluation in long-term care settings in Japan. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2014;14:577–581. doi: 10.1111/ggi.12137. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Japanese Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition . Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Guideline. 3rd ed. Shorinsha; Tokyo, Japan: 2013.
-
- Kurata N. Kaigoshisetsu Zaitakuiryo no Tame no Syokuji Jokyo Kara Michibiku Kusuri no Nomikata Guide. Shakaihokenkenkyusho; Tokyo, Japan: 2023.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

