Detection of Thrombosis Using Soluble C-Type Lectin-like Receptor-2 with D-Dimer Level and Platelet Count
- PMID: 39408040
- PMCID: PMC11477887
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13195980
Detection of Thrombosis Using Soluble C-Type Lectin-like Receptor-2 with D-Dimer Level and Platelet Count
Abstract
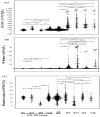
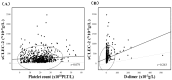
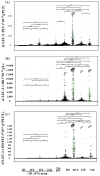
Introduction: Soluble C-type lectin-like receptor -2 (sCLEC-2) has been recognized as a marker of platelet activation, and attention has been drawn to formulas combining sCLEC-2 levels with platelet count and D-dimer levels. Methods: In this study, sCLEC-2 levels, as well as sCLEC-2/platelet count (sCLEC-2/PLT), sCLEC-2 × D-dimer (sCLEC-2xDD), and sCLEc-2xDD/PLT formulas were used to detect thrombotic diseases, including microvascular thrombosis (MVT), arterial thromboembolism (ATE), and venous thromboembolism (VTE), with the aim of evaluating the ability of the three parameters combined in these formulas to diagnose thrombotic diseases. Results: The plasma sCLEC-2 levels were significantly higher in patients with infectious or thrombotic diseases than in those with neither thrombosis nor infection; however, there was no significant difference among patients with infection, ATE, VTE, and MVT; the correlations among sCLEC-2, platelet count, and D-dimer level were poor. The sCLEC-2/PLT ratio was the highest in patients with MVT, and the sCLEC-2 × D-dimer value was higher in patients with MVT and VTE than in those with neither thrombosis nor infection. Although receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis shows the differential diagnosis of thrombotic diseases from non-thrombosis without infection, the sCLEC-2 × D-dimer/platelet count was useful for differential diagnosis among MVT and infection or non-thrombotic diseases. Conclusions: sCLEC-2 is useful for the diagnosis of thrombosis, and the formulas of sCLEC-2 with platelet count or D-dimer are useful for the diagnosis of thrombosis using ROC analyses for the thrombosis group vs. the non-thrombosis group without infection.
Keywords: D-dimer; arterial thrombosis; micro thrombosis; platelet count; sCLEC-2; venous thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The measurements of sCLEC-2 and D-dimer levels were partially supported by the PHC Corporation, of which M.K. is an employee. In all other points, the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stevens S.M., Woller S.C., Baumann Kreuziger L., Doerschug K., Geersing G.J., Klok F.A., King C.S., Murin S., Vintch J.R.E., Wells P.S., et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: Compendium and Review of CHEST Guidelines 2012-2021. Chest. 2024;166:388–404. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2024.03.003. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

