Surgical Experience and Functional Outcomes after Laparoscopic and Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy: Results from a Multi-Institutional Collaboration
- PMID: 39408076
- PMCID: PMC11477761
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13196016
Surgical Experience and Functional Outcomes after Laparoscopic and Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy: Results from a Multi-Institutional Collaboration
Abstract
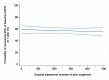
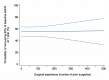
Background: In patients treated with partial nephrectomy, prior evidence showed that peri-operative outcomes, such as complications and ischemia time, improved as a function of the surgical experience of the surgeon, but data on functional outcomes after surgery are still scarce. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data of 4011 patients with a single, unilateral cT1a-b renal mass treated with laparoscopic or robot-assisted partial nephrectomy. The operations were performed by 119 surgeons at 22 participating institutions between 1997 and 2022. Multivariable models investigated the association between surgical experience (number of prior operations) and acute kidney injury (AKI) and recovery of at least 90% of baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) 1 yr after partial nephrectomy. The adjustment for case mix included age, Body Mass Index, preoperative serum creatinine, clinical T stage, PADUA score, warm ischemia time, pathologic tumor size, and year of surgery. Results: A total of 753 (19%) and 3258 (81%) patients underwent laparoscopic and robot-assisted partial nephrectomy, respectively. Overall, 37 (31%) and 55 (46%) surgeons contributed only to laparoscopic and robotic learning curves, respectively, whereas 27 (23%) contributed to the learning curves of both approaches. In the laparoscopic group, 8% and 55% of patients developed AKI and recovered at least 90% of their baseline eGFR, respectively. After adjusting for confounders, we did not find evidence of an association between surgical experience and AKI after laparoscopic partial nephrectomy (odds ratio [OR]: 0.9992; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.9963, 1.0022; p = 0.6). Similar results were found when 1-year renal function was the outcome of interest (OR: 0.9996; 95% CI: 0.9988, 1.0005; p = 0.5). Among patients who underwent robot-assisted partial nephrectomy, AKI occurred in 11% of patients, whereas 54% recovered at least 90% of their baseline eGFR. On multivariable analyses, the relationship between surgical experience and AKI after surgery was not statistically significant (OR: 1.0015; 95% CI: 0.9992, 1.0037; p = 0.2), with similar results when the outcome of interest was renal function one year after surgery (OR: 1.0001; 95% CI: 0.9980, 1.0022; p = 0.9). Virtually the same findings were found on sensitivity analyses. Conclusions: In patients treated with laparoscopic or robot-assisted partial nephrectomy, our data suggest that the surgical experience of the operating surgeon might not be a key determinant of functional recovery after surgery. This raises questions about the use of serum markers to assess functional recovery in patients with two kidneys and opens the discussion on what are the key steps of the procedure that allowed surgeons to achieve optimal outcomes since their initial cases.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; functional outcomes; learning curve; partial nephrectomy; robot-assisted surgery; surgical experience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mihai I., Dura H., Teodoru C.A., Todor S.B., Ichim C., Grigore N., Mohor C.I., Mihetiu A., Oprinca G., Bacalbasa N., et al. Intraoperative Ultrasound: Bridging the Gap between Laparoscopy and Surgical Precision during 3D Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomies. Diagnostics. 2024;14:942. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14090942. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Larcher A., Muttin F., Peyronnet B., De Naeyer G., Khene Z.-E., Dell’Oglio P., Ferreiro C., Schatteman P., Vickers A., D’Hondt F., et al. The Learning Curve for Robot-assisted Partial Nephrectomy: Impact of Surgical Experience on Perioperative Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2019;75:253–256. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.08.042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bravi C.A., Vertosick E., Benfante N., Tin A., Sjoberg D., Hakimi A.A., Touijer K., Montorsi F., Eastham J., Russo P., et al. Impact of Acute Kidney Injury and Its Duration on Long-term Renal Function after Partial Nephrectomy. Eur. Urol. 2019;76:398–403. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.04.040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chawla L.S., Bellomo R., Bihorac A., Goldstein S.L., Siew E.D., Bagshaw S.M., Bittleman D., Cruz D., Endre Z., Fitzgerald R.L., et al. Acute Kidney Disease and Renal Recovery: Consensus Report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nature Publishing Group; New York, NY, USA: 2017. pp. 1–17. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

