Influence of Type 2 Diabetes and Adipose Tissue Dysfunction on Breast Cancer and Potential Benefits from Nutraceuticals Inducible in Microalgae
- PMID: 39408212
- PMCID: PMC11478231
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16193243
Influence of Type 2 Diabetes and Adipose Tissue Dysfunction on Breast Cancer and Potential Benefits from Nutraceuticals Inducible in Microalgae
Abstract
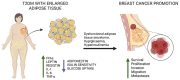
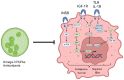
Breast cancer (BC) represents the most prevalent cancer in women at any age after puberty. From a pathogenetic prospective, despite a wide array of risk factors being identified thus far, poor metabolic health is emerging as a putative risk factor for BC. In particular, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) provides a perfect example bridging the gap between poor metabolic health and BC risk. Indeed, T2DM is preceded by a status of hyperinsulinemia and is characterised by hyperglycaemia, with both factors representing potential contributors to BC onset and progression. Additionally, the aberrant secretome of the dysfunctional, hypertrophic adipocytes, typical of obesity, characterised by pro-inflammatory mediators, is a shared pathogenetic factor between T2DM and BC. In this review, we provide an overview on the effects of hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinemia, hallmarks of type 2 diabetes mellitus, on breast cancer risk, progression, treatment and prognosis. Furthermore, we dissect the role of the adipose-tissue-secreted adipokines as additional players in the pathogenesis of BC. Finally, we focus on microalgae as a novel superfood and a source of nutraceuticals able to mitigate BC risk by improving metabolic health and targeting cellular pathways, which are disrupted in the context of T2DM and obesity.
Keywords: adipokines; breast cancer; insulin resistance; microalgae; nutraceuticals; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Mayrovitz H.N. Breast Cancer. Exon Publications; Brisbane, Australia: 2022. - PubMed
-
- Naidu G., Srikanth S., Tiwari M., GJ N.R., Sarita P. Analysis of serum trace elemental content in pre-post chemotherapy breast cancer patients using synchrotron radiation based X-ray fluorescence. Nucl. Part. Phys. Proc. 2023;341:19–21.
-
- Nascimento R.G.d., Otoni K.M. Histological and molecular classification of breast cancer: What do we know? Mastology. 2020;30:1–8. doi: 10.29289/25945394202020200024. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

