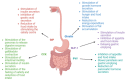
The Impact of Gastrointestinal Hormones on Human Adipose Tissue Function
- PMID: 39408213
- PMCID: PMC11479152
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16193245
The Impact of Gastrointestinal Hormones on Human Adipose Tissue Function
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a global issue, the development of which depends on many interacting factors. Among these, hormones secreted in the gastrointestinal tract play an important role. The aim of this review was to assess the impact of these hormones on the functions of adipose tissue.
Methods: The analysis was based on the latest research concerning both adipose tissue and gastrointestinal hormones.
Results: It was found that these hormones can significantly affect adipose tissue, both directly and indirectly. Some hormones, when secreted in excess, can stimulate adipose tissue formation processes, while others can inhibit them. The impact of hormones depends on the location and type of adipose tissue as well as the physiological state of the body. It should also be noted that no hormone acts in isolation but in close cooperation with other factors.
Conclusions: The relationship between gastrointestinal hormones and adipose tissue, and their role in obesity, is a complex and evolving field of study. Further research is necessary, particularly into the interactions between hormones and other factors, as well as their mutual interactions.
Keywords: CCK; GIP; GLP-1; PYY; adipose tissue; gastrointestinal hormones; ghrelin; hormones; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- OECD . The Heavy Burden of Obesity: The Economics of Prevention. OECD; Paris, France: 2019. OECD Health Policy Studies; p. 256.
-
- World Obesity Federation . Obesity: Missing the 2025 Global Targets. World Obesity Federation; London, UK: 2020. pp. 16–33. Global Trends in Obesity. Trends, Costs and Country Reports.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical