A Multiomics Evaluation of the Countermeasure Influence of 4-Week Cranberry Beverage Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Changes in Innate Immunity
- PMID: 39408218
- PMCID: PMC11479082
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16193250
A Multiomics Evaluation of the Countermeasure Influence of 4-Week Cranberry Beverage Supplementation on Exercise-Induced Changes in Innate Immunity
Abstract
Objectives: This study examined the effect of a 4-week unsweetened cranberry beverage (CRAN) (317 mg polyphenols) versus placebo beverage (PLAC) ingestion (240 mL/day) on moderating exercise-induced changes in innate immunity.
Methods: Participants included 25 male and female non-elite cyclists. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind crossover design was used with two 4-week supplementation periods and a 2-week washout period. Supplementation periods were followed by an intensive 2.25 h cycling bout. Six blood samples were collected before and after supplementation (in an overnight fasted state) and at 0 h, 1.5 h, 3 h, and 24 h post-exercise. Stool and urine samples were collected pre- and post-supplementation. Outcome measures included serum creatine kinase, myoglobin, and cortisol, complete blood counts, plasma untargeted proteomics, plasma-targeted oxylipins, untargeted urine metabolomics, and stool microbiome composition via whole genome shotgun (WGS) sequencing.
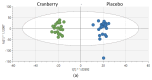
Results: Urine CRAN-linked metabolites increased significantly after supplementation, but no trial differences in alpha or beta microbiota diversity were found in the stool samples. The 2.25 h cycling bout caused significant increases in plasma arachidonic acid (ARA) and 53 oxylipins (FDR q-value < 0.05). The patterns of increase for ARA, four oxylipins generated from ARA-cytochrome P-450 (CYP) (5,6-, 8,9-, 11,12-, and 14,15-diHETrEs), two oxylipins from linoleic acid (LA) and CYP (9,10-DiHOME, 12,13-DiHOME), and two oxylipins generated from LA and lipoxygenase (LOX) (9-HODE, 13-HODE) were slightly but significantly higher for the CRAN versus PLAC trial (all interaction effects, p < 0.05). The untargeted proteomics analysis showed that two protein clusters differed significantly between the CRAN and PLAC trials, with CRAN-related elevations in proteins related to innate immune activation and reduced levels of proteins related to the regulation of the complement cascade, platelet activation, and binding and uptake of ligands by scavenger receptors. No trial differences were found for cortisol and muscle damage biomarkers.
Conclusions: CRAN versus PLAC juice resulted in a significant increase in CRAN-related metabolites but no differences in the gut microbiome. CRAN supplementation was associated with a transient and modest but significant post-exercise elevation in selected oxylipins and proteins associated with the innate immune system.
Keywords: cranberry; exercise; gut microbiome; immunity; metabolomics; oxylipins; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from Ocean Spray. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Christ T., Ringleb M., Haunhorst S., Fennen L., Jordan P.M., Wagner H., Puta C. The acute effects of pre- and mid-exercise carbohydrate ingestion on the immunoregulatory stress hormone release in experienced endurance athletes-a systematic review. Front. Sports Act. Living. 2024;6:1264814. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2024.1264814. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

