Omega-3 Supplementation in Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Patients: Impact on ICU Stay and Hospital Stay-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39408265
- PMCID: PMC11478518
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16193298
Omega-3 Supplementation in Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Patients: Impact on ICU Stay and Hospital Stay-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) is associated with inflammation and complications, potentially leading to prolonged ICU and hospital stays. Omega-3 PUFA has anti-inflammatory properties, thought to potentially reduce complications in CABG patients. This study aims to systematically review and meta-analyze the impact of perioperative omega-3 PUFA supplementation on total ICU and total hospital stays in CABG patients; Methods: Randomized controlled trials examining the effects of omega-3 PUFA supplementation (IV/oral) on ICU and hospital stays in CABG patients were included. Studies were searched for in PubMed, EMBASE, PsychINFO, CINAHL, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trial databases, along with hand searching of reference lists. The quality and risk of bias of the included studies were evaluated by two independent reviewers using the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool. Meta-analysis was performed using fixed or random effects models according to the level of heterogeneity by mean difference with their 95% confidence intervals; Results: Twelve studies were included in the qualitative analysis and seven in the meta-analysis. Omega-3 PUFA was associated with a significant reduction in days of hospital stay (-0.58 (95% CI -1.13, -0.04)). Subgroup analysis showed that only oral omega-3 PUFA supplementation resulted in a statistically significant reduction in length of hospitalization after subgroup analysis with MD -0.6 (95% CI -1.17, -0.04); Conclusions: This study suggests that perioperative omega-3 PUFA supplementation may reduce the length of hospitalization in CABG patients, especially when administered orally. However, the findings should be interpreted cautiously due to the high level of heterogeneity.
Keywords: CABG; ICU; hospital stay; meta-analysis; omega-3 PUFA.
Conflict of interest statement
There was heterogeneity among the studies concerning the sources of funding and conflict of interest disclosures. Five studies explicitly stated that authors had no conflicts of interest [29,42,47,50,51]. In contrast, five studies did not provide any conflict of interest disclosure [43,45,46,48,49,52]. Notably, only one study acknowledged the presence of conflicts of interest [44].
Regarding funding sources, five studies received support from pharmaceutical companies [44,45,47,48,50]. Two studies declared no external funding [42,52], while three studies provided no information regarding funding sources [43,46,49].
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
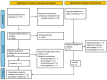



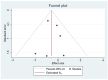
References
-
- Indicators O. Health at a Glance 2009. Health Workers: Psychiatrists. [(accessed on 20 January 2023)]. Available online: http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/docserver/download/fulltext/8109111ec030.pd....
-
- Weiss A.J., Elixhauser A. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs [Internet] Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; Rockville, MA, USA: 2014. Trends in Operating Room Procedures in US Hospitals, 2001–2011: Statistical Brief# 171.
-
- NIH What Is Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting? [(accessed on 20 January 2023)];2022 Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507836/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

