Influence of Mediterranean Diet on Sexual Function in People with Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 39408364
- PMCID: PMC11479179
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16193397
Influence of Mediterranean Diet on Sexual Function in People with Metabolic Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Abstract
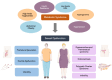
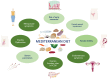
Metabolic syndrome (MS), a cluster of cardiometabolic disorders, and sexual dysfunction are two conditions that impact a large proportion of the general population. Although they can occur independently, they are frequently linked and significantly affect people's quality of life. In recent years, research has increasingly focused on the importance of diet, particularly the Mediterranean diet (MD), in modulating sexual function due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and vasodilatory properties. In this narrative review, we examined the relationship between MS and sexual function in both men and women, with a special emphasis on the MD's therapeutic efficacy in improving sexual dysfunction. In men, MD has been shown to ameliorate erectile dysfunction, as well as several sperm parameters, perhaps leading to improved fertility. On the other hand, adherence to MD has been demonstrated to partially recover several sexual dysfunctions in women, such as those related to their menstrual cycle, menopause, endometriosis, and polycystic ovary syndrome. These favorable effects of MD have been demonstrated in both sexes also among people affected by MS. However, more targeted studies are needed to validate these data for different dietary approaches as well.
Keywords: Mediterranean diet; erectile dysfunction; infertility; libido; menstrual cycle; metabolic syndrome; metabolism; obesity; oxidative stress; sexual function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Noubiap J.J., Nansseu J.R., Lontchi-Yimagou E., Nkeck J.R., Nyaga U.F., Ngouo A.T., Tounouga D.N., Tianyi F.L., Foka A.J., Ndoadoumgue A.L., et al. Global, Regional, and Country Estimates of Metabolic Syndrome Burden in Children and Adolescents in 2020: A Systematic Review and Modelling Analysis. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2022;6:158–170. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00374-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Noubiap J.J., Nansseu J.R., Lontchi-Yimagou E., Nkeck J.R., Nyaga U.F., Ngouo A.T., Tounouga D.N., Tianyi F.L., Foka A.J., Ndoadoumgue A.L., et al. Geographic Distribution of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components in the General Adult Population: A Meta-Analysis of Global Data from 28 Million Individuals. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;188:109924. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109924. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vinciguerra F., Tumminia A., Baratta R., Ferro A., Alaimo S., Hagnäs M., Graziano M., Vigneri R., Frittitta L. Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Children and Adolescents with Metabolically Healthy Obesity: Role of Insulin Sensitivity. Life. 2020;10:127. doi: 10.3390/life10080127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

