Fabrication of Low-Cost Porous Carbon Polypropylene Composite Sheets with High Photothermal Conversion Performance for Solar Steam Generation
- PMID: 39408523
- PMCID: PMC11479202
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16192813
Fabrication of Low-Cost Porous Carbon Polypropylene Composite Sheets with High Photothermal Conversion Performance for Solar Steam Generation
Abstract
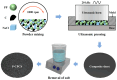
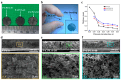
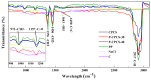
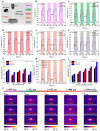
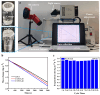
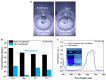
The development of absorber materials with strong light absorption properties and low-cost fabrication processes is highly significant for the application of photothermal conversion technology. In this work, a mixed powder consisting of NaCl, polypropylene (PP), and scale-like carbon flakes was ultrasonically pressed into sheets, and the NaCl was then removed by salt dissolution to obtain porous carbon polypropylene composite sheets (P-CPCS). This process is simple, green, and suitable for the low-cost, large-area fabrication of P-CPCS. P-CPCS has a well-distributed porous structure containing internal and external connected water paths. Under the dual effects of the carbon flakes and porous structure, P-CPCS shows excellent photothermal conversion performance in a broad wavelength range. P-CPCS-40 achieves a high temperature of 128 °C and a rapid heating rate of 12.4 °C/s under laser irradiation (808 nm wavelength, 1.2 W/cm2 power). When utilized for solar steam generation under 1 sun irradiation, P-CPCS-40 achieves 98.2% evaporation efficiency and a 1.81 kg m-2 h-1 evaporation rate. This performance means that P-CPCS-40 outperforms most other previously reported absorbers in terms of evaporation efficiency. The combination of carbon flakes, which provide a photothermal effect, and a porous polymer structure, which provides light-capturing properties, opens up a new strategy for desalination, sewage treatment, and other related fields.
Keywords: desalination; photothermal conversion; porous structure; solar steam generation; ultrasonic pressing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Fan M., You S., Xia J., Zheng W., Zhang H., Liang H., Li X., Li B. An optimized Monte Carlo ray tracing optical simulation model and its applications to line-focus concentrating solar collectors. Appl. Energy. 2018;225:769–781. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.05.067. - DOI
-
- Liu W., Li P., Li X., He Y., An L., Qu D., Wang X., Sun Z. Self-cleaning solar water evaporation device based on polyaniline/TiO2/natural cellulose fibers for contaminant water. Sci. China Mater. 2023;66:1607–1614. doi: 10.1007/s40843-022-2282-9. - DOI
-
- Shi L., Shi Y., Zhuo S., Zhang C., Aldrees Y., Aleid S., Wang P. Multi-functional 3D honeycomb ceramic plate for clean water production by heterogeneous photo-Fenton reaction and solar-driven water evaporation. Nano Energy. 2019;60:222–230. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.03.039. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

