DNA Damage in Moderate and Severe COVID-19 Cases: Relation to Demographic, Clinical, and Laboratory Parameters
- PMID: 39408623
- PMCID: PMC11476890
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910293
DNA Damage in Moderate and Severe COVID-19 Cases: Relation to Demographic, Clinical, and Laboratory Parameters
Abstract
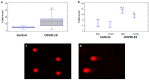
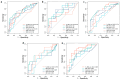
The ability of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to cause DNA damage in infected humans requires its study as a potential indicator of COVID-19 progression. DNA damage was studied in leukocytes of 65 COVID-19 patients stratified by sex, age, and disease severity in relation to demographic, clinical, and laboratory parameters. In a combined group of COVID-19 patients, DNA damage was shown to be elevated compared to controls (12.44% vs. 5.09%, p < 0.05). Severe cases showed higher DNA damage than moderate cases (14.66% vs. 10.65%, p < 0.05), and males displayed more damage than females (13.45% vs. 8.15%, p < 0.05). DNA damage is also correlated with international normalized ratio (INR) (r = 0.471, p < 0.001) and creatinine (r = 0.326, p < 0.05). In addition to DNA damage, severe COVID-19 is associated with age, C-reactive protein (CRP), and creatinine. Receiver operating characteristic analysis identified age, INR, creatinine, DNA damage, and CRP as significant predictors of disease severity, with cut-off values of 72.50 years, 1.46 s, 78.0 µmol/L, 9.72%, and 50.0 mg/L, respectively. The results show that DNA damage correlates with commonly accepted COVID-19 risk factors. These findings underscore the potential of DNA damage as a biomarker for COVID-19 severity, suggesting its inclusion in prognostic assessments to facilitate early intervention and improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: COVID-19; DNA damage; SARS-CoV-2 virus; comet assay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2024.
-
- Carabelli A.M., Peacock T.P., Thorne L.G., Harvey W.T., Hughes J., de Silva T.I., Peacock S.J., Barclay W.S., de Silva T.I., Towers G.J., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variant Biology: Immune Escape, Transmission and Fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023;21:162–177. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00841-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

