Stilbene Treatment Reduces Stemness Features in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Model
- PMID: 39408719
- PMCID: PMC11476666
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910390
Stilbene Treatment Reduces Stemness Features in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Model
Abstract
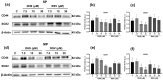
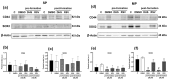
Lung cancer is among the most clinically challenging tumors because of its aggressive proliferation, metastasis, and the presence of cancer stem cells (CSCs). Natural bioactive substances have been used for cancer prevention, and, in particular, resveratrol (RSV), a stilbene-based compound with wide biological properties, has been proposed for chemoprevention. Its lesser-known analogue 4,4'-dihydroxy-trans-stilbene (DHS) has demonstrated superior activity both in cell-based assays and in mouse and zebrafish in vivo models. The present study analyzed the effects of DHS and RSV on A549 lung cancer cells, with a particular focus on stemness features and CSCs, isolated by sorting of the side population (SP). The results show that both stilbenes, especially DHS, strongly inhibited cell cycle progression. A reduction in the S phase was induced by DHS, whereas an increase in this phase was obtained with RSV. In addition, 50% reductions in the clonogenicity and soft agar colony formation were observed with the DHS treatment only. Finally, both stilbenes, especially DHS, reduced stemness marker expression in A549 cells and their sorted SP fraction. Spheroid formation, higher in SP cells than in the main population (MP), was significantly reduced after pretreatment with DHS, which was found to decrease SOX2 levels more than RSV. These findings indicate that stilbenes, and particularly DHS, affect stemness features of A549 cells and the SP fraction, suggesting their potential utility as anticancer agents, either alone or combined with chemotherapeutic drugs.
Keywords: 4,4’-dihydroxy-trans-stilbene; A549 cells; resveratrol; stemness markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Hazafa A., Iqbal M.O., Javaid U., Tareen M.B.K., Amna D., Ramzan A., Piracha S., Naeem M. Inhibitory effect of polyphenols (phenolic acids, lignans, and stilbenes) on cancer by regulating signal transduction pathways: A review. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021;24:432–445. doi: 10.1007/s12094-021-02709-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

