Update on Biomarkers of Chronic Inflammatory Processes Underlying Diabetic Neuropathy
- PMID: 39408723
- PMCID: PMC11476795
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910395
Update on Biomarkers of Chronic Inflammatory Processes Underlying Diabetic Neuropathy
Abstract
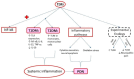
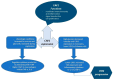
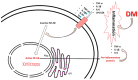
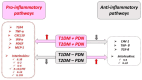
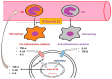
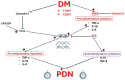
There is an increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM), particularly type 2 DM (T2DM), and its associated complications. T2DM is linked to insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and oxidative stress, which can lead to both macrovascular and microvascular complications, including peripheral diabetic neuropathy (PDN). Inflammatory processes play a key role in the development and progression of T2DM and its complications, with specific markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukins (ILs), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α being associated with increased risk. Other key inflammatory markers such as nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) are activated under hyperglycemic and oxidative stress conditions and contribute to the aggravation of PDN by regulating inflammatory gene expression and enhancing endothelial dysfunction. Other important roles in the inflammatory processes are played by Toll-like receptors (TLRs), caveolin 1 (CAV1), and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP1). There is a relationship between vitamin D deficiency and PDN, highlighting the critical role of vitamin D in regulating inflammation and immune responses. The involvement of macrophages in PDN is also suspected, emphasizing their role in chronic inflammation and nerve damage in diabetic patients. Vitamin D supplementation has been found to reduce neuropathy severity, decrease inflammatory markers, and improve glycemic control. These findings suggest that addressing vitamin D deficiency could offer therapeutic benefits for PDN. These molecular pathways are critical in understanding the pathogenesis of DM complications and may offer potential biomarkers or therapeutic targets including anti-inflammatory treatments, vitamin D supplementation, macrophage phenotype modulation, and lifestyle modifications, aimed at reducing inflammation and preventing PDN. Ongoing and more extensive clinical trials with the aim of investigating anti-inflammatory agents, TNF-α inhibitors, and antioxidants are needed to advance deeper into the understanding and treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy.
Keywords: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4); caveolin 1; diabetic neuropathy; inflammation; type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM); vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C.N., Mbanya J.C., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., Malanda B., Karuranga S., Unwin N., Colagiuri S., Guariguata L., Motala A.A., Ogurtsova K., et al. Global and Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2019 and Projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li Y., Teng D., Shi X., Qin G., Qin Y., Quan H., Shi B., Sun H., Ba J., Chen B., et al. Prevalence of Diabetes Recorded in Mainland China Using 2018 Diagnostic Criteria from the American Diabetes Association: National Cross Sectional Study. BMJ. 2020;369:m997. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m997. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goyal R., Singhal M., Jialal I. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Type 2 Diabetes. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

