Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds Produced by the Intestinal Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 39408727
- PMCID: PMC11477366
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910397
Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds Produced by the Intestinal Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
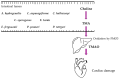
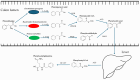
Cardiovascular disease is the main cause of mortality in industrialized countries, with over 500 million people affected worldwide. In this work, the roles of low-molecular-weight metabolites originating from the gut microbiome, such as short-chain fatty acids, hydrogen sulfide, trimethylamine, phenylacetic acid, secondary bile acids, indoles, different gases, neurotransmitters, vitamins, and complex lipids, are discussed in relation to their CVD-promoting or preventing activities. Molecules of mixed microbial and human hepatic origin, such as trimethylamine N-oxide and phenylacetylglutamine, are also presented. Finally, dietary agents with cardioprotective effects, such as probiotics, prebiotics, mono- and poly-unsaturated fatty acids, carotenoids, and polyphenols, are also discussed. A special emphasis is given to their gut microbiota-modulating properties.
Keywords: bile acids; hydrogen sulfide; phenylacetylglutamine; short-chain fatty acid; trimethylamine N-oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tsao C.W., Aday A.W., Almarzooq Z.I., Alonso A., Beaton A.Z., Bittencourt M.S., Boehme A.K., Buxton A.E., Carson A.P., Commodore-Mensah Y., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145:E153–E639. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001052. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ndzie Noah M.L., Adzika G.K., Mprah R., Adekunle A.O., Adu-Amankwaah J., Sun H. Sex—Gender Disparities in Cardiovascular Diseases: The Effects of Estrogen on ENOS, Lipid Profile, and NFATs during Catecholamine Stress. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021;8:639946. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.639946. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Jimenez F., Almahmeed W., Bays H., Cuevas A., Di Angelantonio E., le Roux C.W., Sattar N., Sun M.C., Wittert G., Pinto F.J., et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanistic Insights and Management Strategies. A Joint Position Paper by the World Heart Federation and World Obesity Federation. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2022;29:2218–2237. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwac187. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AYUD/2021/51347/Gobierno del Principado de Asturias
- PID2021-127812OB-I00/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- MCI-21-PID2020-113062RB-100/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
- PRDAS233973MCAL/Asociación Española Contra el Cáncer
- PRE2019-089448/Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

