Basic Guide for Approaching Drug Delivery with Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 39408730
- PMCID: PMC11476574
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910401
Basic Guide for Approaching Drug Delivery with Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
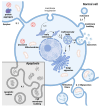
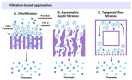
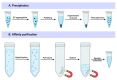
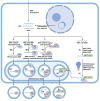
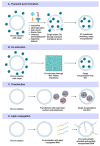
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are natural carriers of biomolecules that play a crucial role in cell-to-cell communication and tissue homeostasis under normal and pathological conditions, including inflammatory diseases and cancer. Since the discovery of the pro-regenerative and immune-modulating properties of EVs, EV-based therapeutics have entered clinical trials for conditions such as myocardial infarction and autoimmune diseases, among others. Due to their unique advantages-such as superior bioavailability, substantial packaging capacity, and the ability to traverse biological barriers-EVs are regarded as a promising platform for targeted drug delivery. However, achieving a sufficient accumulation of therapeutic agents at the target site necessitates a larger quantity of EVs per dose compared to using EVs as standalone drugs. This challenge can be addressed by administering larger doses of EVs, increasing the drug dosage per administration, or enhancing the selective accumulation of EVs at target cells. In this review, we will discuss methods to improve the isolation and purification of EVs, approaches to enhance cargo packaging-including proteins, RNAs, and small-molecule drugs-and technologies for displaying targeting ligands on the surface of EVs to facilitate improved targeting. Ultimately, this guide can be applied to the development of novel classes of EV-based therapeutics and to overcoming existing technological challenges.
Keywords: nanotherapeutics; surface display; targeted drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Welsh J.A., Goberdhan D.C.I., O’Driscoll L., Buzas E.I., Blenkiron C., Bussolati B., Cai H., Di Vizio D., Driedonks T.A.P., Erdbrügger U. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2024;13:e12404. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

