Bovine Neutrophil β-Defensin-5 Provides Protection against Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via Regulating Pulmonary Inflammatory Response and Metabolic Response
- PMID: 39408834
- PMCID: PMC11477005
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910506
Bovine Neutrophil β-Defensin-5 Provides Protection against Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via Regulating Pulmonary Inflammatory Response and Metabolic Response
Abstract
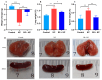
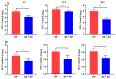
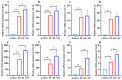
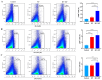
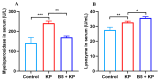
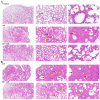
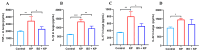
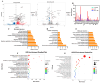
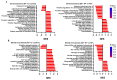
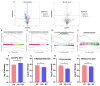
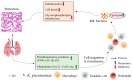
Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae), a kind of zoonotic bacteria, is among the most common antibiotic-resistant pathogens, and it causes nosocomial infections that pose a threat to public health. In this study, the roles of synthetic bovine neutrophil β-defensin-5 (B5) in regulating inflammatory response and metabolic response against multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae infection in a mouse model were investigated. Mice were administrated intranasally with 20 μg of B5 twice and challenged with K. pneumoniae three days after B5 pretreatment. Results showed that B5 failed to directly kill K. pneumoniae in vitro, but it provided effective protection against multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae via decreasing the bacterial load in the lungs and spleen, and by alleviating K. pneumoniae-induced histopathological damage in the lungs. Furthermore, B5 significantly enhanced the mRNA expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, Cxcl1, Cxcl5, Ccl17, and Ccl22 and obviously enhanced the rapid recruitment of macrophages and dendritic cells in the lungs in the early infection phase, but significantly down-regulated the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-17 in the lungs in the later infection phase. Moreover, RNA-seq results showed that K. pneumoniae infection activated signaling pathways related to natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity, IL-17 signaling pathway, inflammatory response, apoptosis, and necroptosis in the lungs, while B5 inhibited these signaling pathways. Additionally, K. pneumoniae challenge led to the suppression of glycerophospholipid metabolism, the phosphotransferase system, the activation of microbial metabolism in diverse environments, and metabolic pathways in the lungs. However, B5 significantly reversed these metabolic responses. Collectively, B5 can effectively regulate the inflammatory response caused by K. pneumoniae and offer protection against K. pneumoniae. B5 may be applied as an adjuvant to the existing antimicrobial therapy to control multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae infection. Our study highlights the potential of B5 in enhancing pulmonary bacterial clearance and alleviating K. pneumoniae-caused inflammatory damage.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; bovine neutrophil β-defensin-5; inflammatory response; metabolic response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SKAP2 is required for defense against K. pneumoniae infection and neutrophil respiratory burst.Elife. 2020 Apr 30;9:e56656. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56656. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32352382 Free PMC article.
-
Both TRIF- and MyD88-dependent signaling contribute to host defense against pulmonary Klebsiella infection.J Immunol. 2009 Nov 15;183(10):6629-38. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901033. Epub 2009 Oct 21. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19846873 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal B5 promotes mucosal defence against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae via ameliorating early immunosuppression.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2316459. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2316459. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38378464 Free PMC article.
-
Topical adjunctive treatment with flagellin augments pulmonary neutrophil responses and reduces bacterial dissemination in multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 4;15:1450486. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1450486. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39295863 Free PMC article.
-
The Long Pentraxin PTX3 Controls Klebsiella Pneumoniae Severe Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 May 20;12:666198. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.666198. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’neill J. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. Tackling a Global Health Crisis: Rapid Diagnostics: Stopping Unnecessary Use of Antibiotics. Indep. Rev. AMR. 2015:1–36.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

