Immunomodulatory Effect of Adipose Stem Cell-Derived Extra-Cellular Vesicles on Cytokine Expression and Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Asthma
- PMID: 39408853
- PMCID: PMC11477288
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910524
Immunomodulatory Effect of Adipose Stem Cell-Derived Extra-Cellular Vesicles on Cytokine Expression and Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Asthma
Abstract
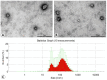
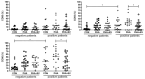
Although mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) are as effective as MSCs in the suppression of allergic airway inflammation, few studies have evaluated the immunomodulatory capacity of MSC-derived EVs in patients with asthma. Thus, we assessed the effects of adipose stem cell (ASC)-derived EVs on cytokine expression and regulatory T cells (Tregs) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of asthmatic patients. PBMCs (1 × 106 cells/mL) were isolated from asthmatic patient and healthy controls and co-cultured with 1 μg/mL of ASC-derived EVs. Th (T helper) 1-, Th2-, and Treg-related cytokine expression, fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ T cells, and co-stimulatory molecules were analyzed before and after ASC-derived EV treatment. The expression levels of IL-4 and costimulatory molecules such as CD83 and CD86 were significantly higher in PBMCs of asthmatic patients than in control PBMCs. However, ASC-derived EV treatment significantly decreased the levels of interleukin (IL)-4 and co-stimulatory molecules such as CD83 and CD86 in the phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated PBMC of asthmatic patients. Furthermore, ASC-derived EVs remarkably increased the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) levels and expression of Tregs in the PBMC of asthmatic patients. ASC-derived EVs induce Treg expansion and have immunomodulatory effects by downregulating IL-4 and upregulating TGF-β in PBMCs of asthmatic patients.
Keywords: T lymphocytes; asthma; extracellular vesicles; immunosuppression therapy; mesenchymal stem cells; regulatory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

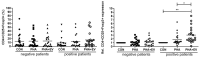
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

