The Relationship between Vascular Biomarkers (Serum Endocan and Endothelin-1), NT-proBNP, and Renal Function in Chronic Kidney Disease, IgA Nephropathy: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39408883
- PMCID: PMC11476882
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910552
The Relationship between Vascular Biomarkers (Serum Endocan and Endothelin-1), NT-proBNP, and Renal Function in Chronic Kidney Disease, IgA Nephropathy: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
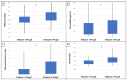
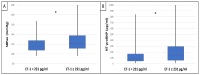
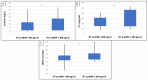
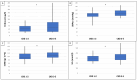
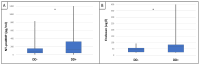
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common primary glomerular disease. Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is one of the strongest vasoconstrictor materials in the blood. The N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is associated with renal function and poor outcomes in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Serum endocan is a biomarker associated with proinflammatory cytokines, and the increase in the serum level plays a critical role in inflammatory, proliferative, and neovascularization processes and is associated with poor cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD too. Identifying high-risk patients using biomarkers could help to optimize their treatment. Ninety patients with biopsy-confirmed IgAN were included in the study (50 males/40 females, mean age: 54.9 ± 14.4 years). Serum endocan, ET-1, and NT-proBNP were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. Echocardiography was performed, and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV) was measured by SphygmoCor in this cross-sectional study. Patients were divided into two groups based on serum endocan median level (cut-off: 44 ug/L). There was significantly higher aorta systolic blood pressure (SBPao) (p = 0.013), NT-proBNP (p = 0.028), albumin/creatinine ratio (p = 0.036), and uric acid (p = 0.045) in the case of the higher endocan group compared to the lower. There was also significantly higher SBPao (p = 0.037) and NT-proBNP (p = 0.038) in the case of higher endothelin-1 (ET-1) levels compared to the lower (cut-off: 231 pg/mL) group by the two-sample t-test. Then, we divided the patients into two groups based on the eGFR (CKD 1-2 vs. CKD 3-5). The levels of serum endocan, NT-proBNP, cfPWV, SBPao, left ventricular mass index (LVMI), uric acid, and albuminuria were significantly higher in the CKD 3-5 group compared to the CKD 1-2 group. The serum endocan and NT-proBNP levels were significantly higher in the diastolic dysfunction group (p = 0.047, p = 0.015). There was a significant increase in serum endocan levels (CKD 1 vs. CKD 5; p = 0.008) with decreasing renal function. In IgAN, vascular biomarkers (endocan, ET-1) may play a role in endothelial dysfunction through vascular damage and elevation of SBPao. Serum endocan, ET-1, and NT-proBNP biomarkers may help to identify IgAN patients at high risk.
Keywords: IgA nephropathy; NT-proBNP; chronic kidney disease; endocan; endothelin-1; renal function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

