Identification and Functional Analysis of Ras-Related Associated with Diabetes Gene (rrad) in Edwardsiella piscicida-Resistant Individuals of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)
- PMID: 39408905
- PMCID: PMC11476895
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910532
Identification and Functional Analysis of Ras-Related Associated with Diabetes Gene (rrad) in Edwardsiella piscicida-Resistant Individuals of Japanese Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus)
Abstract
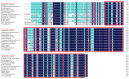
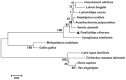
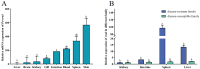
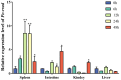
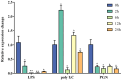
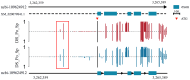
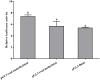
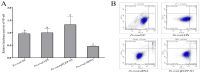
Ras-related associated with diabetes (RRAD) is a member of the Ras GTPase superfamily that plays a role in several cellular functions, such as cell proliferation and differentiation. In particular, the superfamily acts as an NF-κB signaling pathway inhibitor and calcium regulator to participate in the immune response pathway. A recent transcriptome study revealed that rrad was expressed in the spleen of disease-resistant Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) individuals compared with disease-susceptible individuals, and the results were also verified by qPCR. Thus, the present study aimed to explore how rrad regulates antimicrobial immunity via the NF-κB pathway. First, the coding sequence of P. olivaceus rrad was identified. The sequence was 1092 bp in length, encoding 364 amino acids. Based on phylogenetic and structural relationship analyses, P. olivaceus rrad appeared to be more closely related to teleosts. Next, rrad expression differences between disease-resistant and disease-susceptible individuals in immune-related tissues were evaluated, and the results revealed that rrad was expressed preferentially in the spleen of disease-resistant individuals. In response to Edwardsiella piscicida infection, rrad expression in the spleen changed. In vitro, co-culture was carried out to assess the hypo-methylated levels of the rrad promoter in the disease-resistant spleen, which was consistent with the high mRNA expression. The siRNA-mediated knockdown of rrad performed with the gill cell line of P. olivaceus affected many rrad-network-related genes, i.e., dcp1b, amagt, rus1, rapgef1, ralbp1, plce1, rasal1, nckipsd, prkab2, cytbc-1, sh3, and others, as well as some inflammation-related genes, such as bal2 and Il-1β. In addition, flow cytometry analysis showed that rrad overexpression was more likely to induce cell apoptosis, with establishing a link between rrad's function and its potential roles in regulating the NF-κB pathway. Thus,. the current study provided some clarity in terms of understanding the immune response about rrad gene differences between disease-resistant and disease-susceptible P. olivaceus individuals. This study provides a molecular basis for fish rrad gene functional analysis and may serve as a reference for in-depth of bacterial disease resistance of teleost.
Keywords: Japanese flounder; NF-κB; RNAi; disease-resistant and disease-susceptible individuals; methylation; rrad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and functional analysis of dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatase 6 gene (dusp6) in response to immune challenges in Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 Jan;60:411-419. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27940366
-
Identification and characterization of a novel NOD-like receptor family CARD domain containing 3 gene in response to extracellular ATP stimulation and its role in regulating LPS-induced innate immune response in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) head kidney macrophages.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Mar;50:79-90. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.01.029. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26820104
-
Cloning and characterization of apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD domain (ASC) gene from Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Jul;54:294-301. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.022. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27103005
-
Identification and characterization of ATP-gated P2X2 receptor gene dominantly expressed in the Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) head kidney macrophages.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Jul;54:312-21. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.04.020. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27103003
-
Nonconservation of TLR5 activation site in Edwardsiella tarda flagellin decreases expression of interleukin-1β and NF-κB genes in Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Apr;87:765-771. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.02.024. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30776541
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

