Recombinant Influenza A Viruses Expressing Reporter Genes from the Viral NS Segment
- PMID: 39408912
- PMCID: PMC11476892
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910584
Recombinant Influenza A Viruses Expressing Reporter Genes from the Viral NS Segment
Abstract
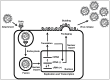
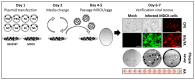
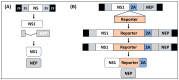
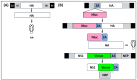
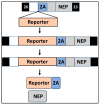
Studying influenza A viruses (IAVs) requires secondary experimental procedures to detect the presence of the virus in infected cells or animals. The ability to generate recombinant (r)IAV using reverse genetics techniques has allowed investigators to generate viruses expressing foreign genes, including fluorescent and luciferase proteins. These rIAVs expressing reporter genes have allowed for easily tracking viral infections in cultured cells and animal models of infection without the need for secondary approaches, representing an excellent option to study different aspects in the biology of IAV where expression of reporter genes can be used as a readout of viral replication and spread. Likewise, these reporter-expressing rIAVs provide an excellent opportunity for the rapid identification and characterization of prophylactic and/or therapeutic approaches. To date, rIAV expressing reporter genes from different viral segments have been described in the literature. Among those, rIAV expressing reporter genes from the viral NS segment have been shown to represent an excellent option to track IAV infection in vitro and in vivo, eliminating the need for secondary approaches to identify the presence of the virus. Here, we summarize the status on rIAV expressing traceable reporter genes from the viral NS segment and their applications for in vitro and in vivo influenza research.
Keywords: NS segment; fluorescence; luminescence; plasmid-based reverse genetics; recombinant influenza A virus; replication-competent reporter-expressing influenza A virus; reporter genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

