Polyphenols as the Main Compounds Influencing the Antioxidant Effect of Honey-A Review
- PMID: 39408935
- PMCID: PMC11477350
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910606
Polyphenols as the Main Compounds Influencing the Antioxidant Effect of Honey-A Review
Abstract
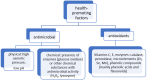
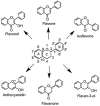
Honey is one of the most valuable components of the human diet. It is considered to be a functional food with health-promoting properties. Honey has bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects; is used to treat wounds and ulcers; relieves stress; supports the treatment of diseases of the digestive and respiratory systems; improves kidney function; and aids in convalescence. The healing and prophylactic effects of honey are closely related to its chemical composition. According to the literature, honey contains over 300 substances belonging to various groups of chemical compounds, some with antioxidant activity, including vitamins and phenolic compounds, mainly flavonoids and phenolic acids. This article provides insight into honey's chemical composition and its pro-health activities. The antioxidant properties of honey were prioritized.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; bioactive substances; phenolic compounds; pro-health properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- DIRECTIVE2014/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 May 2014 Amending Council Directive 2001/110/EC Relating to Honey, Official Journal of the European Union L 164/1. 2014.
-
- Laaroussi H., Bouddine T., Bakour M., Ousaaid D., Lyoussi B. Physicochemical Properties, Mineral Content, Antioxidant Activities, and Microbiological Quality of Bupleurum spinosum Gouan Honey from the Middle Atlas in Morocco. J. Food Qual. 2020;2020:7609454. doi: 10.1155/2020/7609454. - DOI
-
- Bobis O., Moise A.R., Ballesteros I., Reyes E.S., Durán S.S., Sánchez-Sánchez J., Cruz-Quintana S., Giampieri F., Battino M., Alvarez-Suarez J.M. Eucalyptus Honey: Quality Parameters, Chemical Composition and Health-Promoting Properties. Food Chem. 2020;325:126870. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126870. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boussaid A., Chouaibi M., Rezig L., Hellal R., Donsì F., Ferrari G., Hamdi S. Physicochemical and Bioactive Properties of Six Honey Samples from Various Floral Origins from Tunisia. Arab. J. Chem. 2018;11:265–274. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.08.011. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical