Transpulmonary Plasma Endothelin-1 Arterial:Venous Ratio Differentiates Survivors from Non-Survivors in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- PMID: 39408968
- PMCID: PMC11476705
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910640
Transpulmonary Plasma Endothelin-1 Arterial:Venous Ratio Differentiates Survivors from Non-Survivors in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Abstract
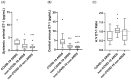
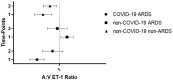
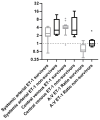
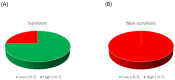
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a potent vasoconstrictor produced by endothelial cells and cleared from circulating blood mainly in the pulmonary vasculature. In a healthy pulmonary circulation, the rate of local production of ET-1 is less than its rate of clearance. In the present study, we aimed to investigate whether the abnormal pulmonary circulatory handling of ET-1 relates to poor clinical outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). To this end, central venous and systemic arterial ET-1 plasma levels were simultaneously measured on Days 1 and 3 following ICU admission in mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients with ARDS (COVID-19 ARDS, N = 18). Central venous and systemic arterial ET-1 plasma levels were also measured in two distinct SARS-CoV-2-negative mechanically ventilated critically ill patient groups, matched for age, sex, and critical illness severity, with ARDS (non-COVID-19 ARDS, N = 14) or without ARDS (non-COVID-19 non-ARDS, N = 20). Upon ICU admission, COVID-19-induced ARDS patients had higher systemic arterial and central venous ET-1 levels compared to the non-COVID-19 ARDS and non-COVID-19 non-ARDS patients (p < 0.05), yet a normal systemic arterial:central venous (A:V) ET-1 ratio [0.63 (0.49-1.02)], suggesting that pulmonary ET-1 clearance is intact in these patients. On the other hand, the non-COVID-19 ARDS patients demonstrated abnormal ET-1 handling [A:V ET-1 ratio 1.06 (0.93-1.20)], while the non-COVID-19 non-ARDS group showed normal ET-1 handling [0.79 (0.52-1.11)]. On Day 3, the A:V ratio in all three groups was <1. When the COVID-19 ARDS patients were divided based on 28-day ICU mortality, while their systemic arterial and central venous levels did not differ, the A:V ET-1 ratio was statistically significantly higher upon ICU admission in the non-survivors [0.95 (0.78-1.34)] compared to the survivors [0.57 (0.48-0.92), p = 0.027]. Our results highlight the potential importance of ET-1 as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target in critically ill COVID-19 patients. The elevated A:V ET-1 ratio in non-survivors suggests that the early disruption of pulmonary ET-1 handling may be a key marker of poor prognosis.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; clearance; endothelin-1; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Grasselli G., Zangrillo A., Zanella A., Antonelli M., Cabrini L., Castelli A., Cereda D., Coluccello A., Foti G., Fumagalli R., et al. Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA. 2020;323:1574–1581. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.5394. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

