Cordyceps militaris Grown on Germinated Rhynchosia nulubilis (GRC) Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticle (GCN) Suppresses Particulate Matter (PM)-Induced Lung Inflammation in Mice
- PMID: 39408971
- PMCID: PMC11477187
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910642
Cordyceps militaris Grown on Germinated Rhynchosia nulubilis (GRC) Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticle (GCN) Suppresses Particulate Matter (PM)-Induced Lung Inflammation in Mice
Abstract
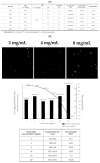
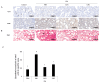
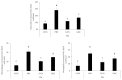
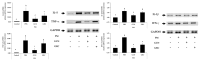
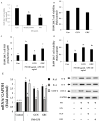
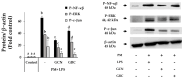
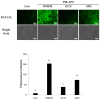
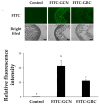
Cordyceps militaris grown on germinated Rhynchosia nulubilis (GRC) exerts various biological effects, including anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, and immune-regulatory effects. In this study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of GRC encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles (CN) against particulate matter (PM)-induced lung inflammation. Optimal CN (CN6) (CHI: TPP w/w ratio of 4:1; TPP pH 2) exhibited a zeta potential of +22.77 mV, suitable for GRC encapsulation. At different GRC concentrations, higher levels (60 and 120 mg/mL) led to increased negative zeta potential, enhancing stability. The optimal GRC concentration for maximum entrapment (31.4 ± 1.35%) and loading efficiency (7.6 ± 0.33%) of GRC encapsulated in CN (GCN) was 8 mg/mL with a diameter of 146.1 ± 54 nm and zeta potential of +30.68. In vivo studies revealed that administering 300 mg/kg of GCN significantly decreased the infiltration of macrophages and T cells in the lung tissues of PM-treated mice, as shown by immunohistochemical analysis of CD4 and F4/80 markers. Additionally, GCN ameliorated PM-induced lung tissue damage, inflammatory cell infiltration, and alveolar septal hypertrophy. GCN also decreased total cells and neutrophils, showing notable anti-inflammatory effects in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from PM-exposed mice, compared to GRC. Next the anti-inflammatory properties of GCN were further explored in PM- and LPS-exposed RAW264.7 cells; it significantly reduced PM- and LPS-induced cell death, NO production, and levels of inflammatory cytokine mRNAs (IL-1β, IL-6, and COX-2). GCN also suppressed NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathways by reducing levels of p-NF-κB, p-ERK, and p-c-Jun proteins, indicating its potential in managing PM-related inflammatory lung disease. Furthermore, GCN significantly reduced PM- and LPS-induced ROS production. The enhanced bioavailability of GRC components was demonstrated by an increase in fluorescence intensity in the intestinal absorption study using FITC-GCN. Our data indicated that GCN exhibited enhanced bioavailability and potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in cells and in vivo, making it a promising candidate for mitigating PM-induced lung inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: C. militaris grown on germinated R. nulubilis; Chitosan nanoparticles; particulate matter anti-inflammatory activity; respiratory disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Kyu-Ree Dhong was employed by the company Magicbullettherapeutics Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wang T., Wang L., Moreno-Vinasco L., Lang G.D., Siegler J.H., Mathew B., Usatyuk P.V., Samet J.M., Geyh A.S., Breysse P.N. Particulate matter air pollution disrupts endothelial cell barrier via calpain-mediated tight junction protein degradation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012;9:35. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-9-35. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dai X., Liu H., Chen D., Zhang J. Association between ambient particulate matter concentrations and hospitalization for ischemic heart disease (I20-I25, ICD-10) in China: A multicity case-crossover study. Atmos. Environ. 2018;186:129–135. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.05.033. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

