Phospholipids, Sphingolipids, and Cholesterol-Derived Lipid Mediators and Their Role in Neurological Disorders
- PMID: 39409002
- PMCID: PMC11476704
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910672
Phospholipids, Sphingolipids, and Cholesterol-Derived Lipid Mediators and Their Role in Neurological Disorders
Abstract
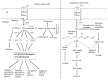
Neural membranes are composed of phospholipids, sphingolipids, cholesterol, and proteins. In response to cell stimulation or injury, the metabolism of lipids generates various lipid mediators, which perform many cellular functions. Thus, phospholipids release arachidonic acid or docosahexaenoic acid from the sn-2 position of the glycerol moiety by the action of phospholipases A2. Arachidonic acid is a precursor for prostaglandins, leukotrienes, thromboxane, and lipoxins. Among these mediators, prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxane produce neuroinflammation. In contrast, lipoxins produce anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving effects. Prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and thromboxane are also involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, blood clotting, and blood vessel permeability. In contrast, DHA-derived lipid mediators are called specialized pro-resolving lipid metabolites (SPMs). They include resolvins, protectins, and maresins. These mediators regulate immune function by producing anti-inflammatory, pro-resolving, and cell protective effects. Sphingolipid-derived metabolites are ceramide, ceramide1-phosphate, sphingosine, and sphingosine 1 phosphate. They regulate many cellular processes, including enzyme activities, cell migration and adhesion, inflammation, and immunity. Cholesterol is metabolized into hydroxycholesterols and 7-ketocholesterol, which not only disrupts membrane fluidity, but also promotes inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. These processes lead to cellular damage.
Keywords: 4-hydroxyhexanal; 4-hydroxynonal; 7-ketocholesterol; arachidonic acid; ceramide-1-phosphate; docosahexaenoic acid; hydroxycholesterol; isoprostane; leukotrienes; lipoxins; maresins; neuroprostane; phospholipids; prostaglandins; protectins; resolvins; sphingosine; sphingosine 1-phosphate; thromboxane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Farooqui A.A., Horrocks L.A. Glycerophospholipids in Brain. Springer Science + Business Media, LLC; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2007.
-
- Farooqui A.A. Hot Topics in Neural Membrane Lipidology. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

