Role of Na+-K+ ATPase Alterations in the Development of Heart Failure
- PMID: 39409137
- PMCID: PMC11476929
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910807
Role of Na+-K+ ATPase Alterations in the Development of Heart Failure
Abstract
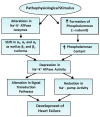
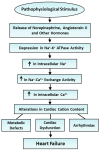
Na+-K+ ATPase is an integral component of cardiac sarcolemma and consists of three major subunits, namely the α-subunit with three isoforms (α1, α2, and α3), β-subunit with two isoforms (β1 and β2) and γ-subunit (phospholemman). This enzyme has been demonstrated to transport three Na and two K ions to generate a trans-membrane gradient, maintain cation homeostasis in cardiomyocytes and participate in regulating contractile force development. Na+-K+ ATPase serves as a receptor for both exogenous and endogenous cardiotonic glycosides and steroids, and a signal transducer for modifying myocardial metabolism as well as cellular survival and death. In addition, Na+-K+ ATPase is regulated by different hormones through the phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of phospholemman, which is tightly bound to this enzyme. The activity of Na+-K+ ATPase has been reported to be increased, unaltered and depressed in failing hearts depending upon the type and stage of heart failure as well as the association/disassociation of phospholemman and binding with endogenous cardiotonic steroids, namely endogenous ouabain and marinobufagenin. Increased Na+-K+ ATPase activity in association with a depressed level of intracellular Na+ in failing hearts is considered to decrease intracellular Ca2+ and serve as an adaptive mechanism for maintaining cardiac function. The slight to moderate depression of Na+-K+ ATPase by cardiac glycosides in association with an increased level of Na+ in cardiomyocytes is known to produce beneficial effects in failing hearts. On the other hand, markedly reduced Na+-K+ ATPase activity associated with an increased level of intracellular Na+ in failing hearts has been demonstrated to result in an intracellular Ca2+ overload, the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias and depression in cardiac function during the development of heart failure. Furthermore, the status of Na+-K+ ATPase activity in heart failure is determined by changes in isoform subunits of the enzyme, the development of oxidative stress, intracellular Ca2+-overload, protease activation, the activity of inflammatory cytokines and sarcolemmal lipid composition. Evidence has been presented to show that marked alterations in myocardial cations cannot be explained exclusively on the basis of sarcolemma alterations, as other Ca2+ channels, cation transporters and exchangers may be involved in this event. A marked reduction in Na+-K+ ATPase activity due to a shift in its isoform subunits in association with intracellular Ca2+-overload, cardiac energy depletion, increased membrane permeability, Ca2+-handling abnormalities and damage to myocardial ultrastructure appear to be involved in the progression of heart failure.
Keywords: Na+-K+ ATPase isoforms; cardiac Na+-K+ ATPase; cardiac dysfunction; endogenous steroids; heart failure; myocardial cation content; phospholemman phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ziegelhoffer A., Kjeldsen K., Bundgaard H., Breier A., Vrbjarm N., Dzurba A. Na, K-ATPase in the myocardium: Molecular principles, functional and clinical aspects. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2000;19:9–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

