Exploiting Translation Machinery for Cancer Therapy: Translation Factors as Promising Targets
- PMID: 39409166
- PMCID: PMC11477148
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms251910835
Exploiting Translation Machinery for Cancer Therapy: Translation Factors as Promising Targets
Abstract
Eukaryotic protein translation has slowly gained the scientific community's attention for its advanced and powerful therapeutic potential. However, recent technical developments in studying ribosomes and global translation have revolutionized our understanding of this complex multistep process. These developments have improved and deepened the current knowledge of mRNA translation, sparking excitement and new possibilities in this field. Translation factors are crucial for maintaining protein synthesis homeostasis. Since actively proliferating cancer cells depend on protein synthesis, dysregulated protein translation is central to tumorigenesis. Translation factors and their abnormal expressions directly affect multiple oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Recently, small molecules have been used to target translation factors, resulting in translation inhibition in a gene-specific manner, opening the door for developing translation inhibitors that can lead to novel chemotherapeutic drugs for treating multiple cancer types caused by dysregulated translation machinery. This review comprehensively summarizes the involvement of translation factors in tumor progression and oncogenesis. Also, it sheds light on the evolution of translation factors as novel drug targets for developing future therapeutic drugs for treating cancer.
Keywords: cancer therapeutics; drug target; eIF1; eIF4F; small-molecule inhibitors; translation initiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
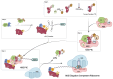
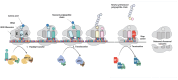
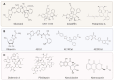
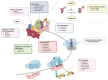
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

