Sensors in Bone: Technologies, Applications, and Future Directions
- PMID: 39409211
- PMCID: PMC11478373
- DOI: 10.3390/s24196172
Sensors in Bone: Technologies, Applications, and Future Directions
Abstract
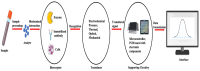
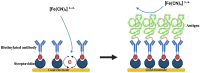
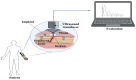
Osteoporosis, a prevalent ailment worldwide, compromises bone strength and resilience, particularly afflicting the elderly population. This condition significantly heightens susceptibility to fractures even from trivial incidents, such as minor falls or impacts. A major challenge in diagnosing osteoporosis is the absence of discernible symptoms, allowing osteoporosis to remain undetected until the occurrence of a fracture event. Early symptom detection and swift diagnosis are critical for preventing severe issues related to bone diseases. Assessing bone turnover markers aids in identifying, diagnosing, and monitoring these conditions, guiding treatment decisions. However, conventional techniques for measuring bone mineral density are costly, time-consuming, and require specialized expertise. The integration of sensor technologies into medical practices has transformed how we monitor, diagnose, and treat various health conditions, including bone health and orthopedics. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of sensor technologies used in bone, covering their integration with bone tissue, various applications, recent advancements, challenges, and future directions.
Keywords: biomechanical sensors; biosensors; bone; bone biomarkers; osteoblasts; osteoclasts; osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
J.-H.S. is a scientific cofounder of AAVAA Therapeutics and holds equity in this company. Other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

