Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the WRKY Transcription Factor Family Associated with Leaf Senescence in Alfalfa
- PMID: 39409595
- PMCID: PMC11478923
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13192725
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the WRKY Transcription Factor Family Associated with Leaf Senescence in Alfalfa
Abstract
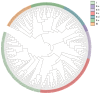
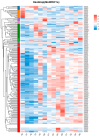
Leaves are the most significant parts of forage crops such as alfalfa. Senescence is the terminal stage of leaf development and is controlled by an integrated myriad of endogenous signals and environmental stimuli. WRKY transcription factors (TFs) play essential roles in regulating leaf senescence; however, only a few studies on the analysis and identification of the WRKY TF family in Medicago Sativa have been reported. In this study, we identified 198 WRKY family members from the alfalfa (M. sativa L.) cultivar 'XinjiangDaye' using phylogenetic analysis and categorized them into three subfamilies, Groups I, II, and III, based on their structural characteristics. Group II members were further divided into five subclasses. In addition, several hormone- and stress-related cis-acting elements were identified in the promoter regions of MsWRKYs. Furthermore, 14 aging-related MsWRKYs genes from a previous transcriptome in our laboratory were selected for RT-qPCR validation of their expression patterns, and subsequently cloned for overexpression examination. Finally, MsWRKY5, MsWRKY66, MsWRKY92, and MsWRKY141 were confirmed to cause leaf yellowing in Nicotiana benthaminana using a transient expression system. Our findings lay a groundwork for further studies on the mechanism of M. sativa leaf aging and for the creation of new germplasm resources.
Keywords: Medicago sativa; WRKY; expression profile; leaf senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

