Thyme and Oregano Oil Potential Therapeutics against Malathion Toxicity through Biochemical, Histological, and Cytochrome P450 1A2 Activities in Male Wistar Rats
- PMID: 39409863
- PMCID: PMC11475483
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14192914
Thyme and Oregano Oil Potential Therapeutics against Malathion Toxicity through Biochemical, Histological, and Cytochrome P450 1A2 Activities in Male Wistar Rats
Abstract
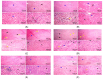
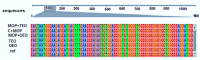
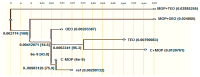
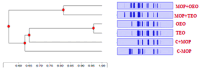
The widespread use of malathion may offer several hazards to humans and animals; additionally, many medicinal plants provide what is known as a broad antitoxicity treatment. This study was carried out to investigate hazardous biochemical and histological reactions to MOP and evaluate the effectiveness of TEO and OEO essential oils in restoring normal physiological conditions after MOP exposure by measuring enzyme-specific activity for Cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2). One hundred and twenty rats were divided into six groups of twenty animals each: (i) C - MOP served as the control group, (ii) C + MOP treated with 5 mg/kg/BW of Malathion-D10, (iii) TEO treated with 100 mg/kg/BW of oregano essential oil, (iv) TEO treated with 100 mg/kg/BW of thyme essential oil, (v) MOP + OEO treated with 5 mg/kg/BW of Malathion-D10 and 100 mg/kg/BW of oregano essential oil, and (vi) MOP + TEO treated with 5 mg/kg/BW of Malathion-D10 and 100 mg/kg/BW of thyme essential oil. The results indicated the protective effects of OEO and TEO against MOP-induced weight loss. Additionally, there was a significant improvement in ALT, AST, and ALK-Ph after being treated with OEO and TEO, either alone or after MOP exposure. Also, treatment with OEO and TEO ameliorated these oxidative stress parameters, indicating their antioxidative properties. A histopathological examination of liver tissues showed reduced hepatocellular damage and improved liver architecture in the OEO and TEO, both alone and in combination with MOP, and protective effects were more pronounced in the TEO-treated groups. However, the results indicated that TEO was more effective than OEO in increasing CYP1A2 expression and alleviating MOP-induced toxicity. Specifically, TEO showed higher protein expression and therapeutic action in reducing liver damage. In conclusion, these findings suggest that OEO and TEO may be potent therapeutic agents against MOP toxicity, offering protective effects by enhancing CYP1A2 activity and mitigating organ damage. Such knowledge would be an important step toward developing potentially unique treatment options for natural antitoxins.
Keywords: antitoxic; cytochrome P450; malathion; oregano essential oil; thyme essential oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures



References
-
- Paul B.T., Anita K.P., Clement G.Y., Pamela D.M. Environmental Exposure and Health Effects Associated with Malathion Toxicity. In: Marcelo L.L., Sonia S., editors. Toxicity and Hazard of Agrochemicals. IntechOpen; Rijeka, Croatia: 2015. Chapter 3.
-
- Guberman VerPloeg S.L., Yoon S., Alvarez S.L., Flynn J.H., Collins D., Griffin R.J., Sheesley R.J., Usenko S. Atmospheric Transport of Adulticides Used to Control Mosquito Populations across an Urban Metropolitan Area. Atmosphere. 2023;14:1495. doi: 10.3390/atmos14101495. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

