Present and Future of Immunotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39409871
- PMCID: PMC11475478
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16193250
Present and Future of Immunotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
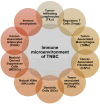
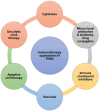
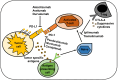
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) lacks the expression of estrogen receptors (ERs), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and progesterone receptors (PRs). TNBC has the poorest prognosis among breast cancer subtypes and is more likely to respond to immunotherapy due to its higher expression of PD-L1 and a greater percentage of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Immunotherapy has revolutionized TNBC treatment, especially with the FDA's approval of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) combined with chemotherapy for advanced cases, opening new avenues for treating this deadly disease. Although immunotherapy can significantly improve patient outcomes in a subset of patients, achieving the desired response rate for all remains an unmet clinical goal. Strategies that enhance responses to immune checkpoint blockade, including combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy, molecularly targeted therapy, or radiotherapy, may improve response rates and clinical outcomes. In this review, we provide a short background on TNBC and immunotherapy and explore the different types of immunotherapy strategies that are currently being evaluated in TNBC. Additionally, we review why combination strategies may be beneficial, provide an overview of the combination strategies, and discuss the novel immunotherapeutic opportunities that may be approved in the near future for TNBC.
Keywords: TNBC; chemotherapy; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; radiation therapy; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
S.S., S.T., S.N.: no COIs; C.S.: Exact Sciences (paid consultant—no direct conflict).
Figures
References
-
- Bauer K.R., Brown M., Cress R.D., Parise C.A., Caggiano V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: A population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer. 2007;109:1721–1728. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22618. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liedtke C., Mazouni C., Hess K.R., Andre F., Tordai A., Mejia J.A., Symmans W.F., Gonzalez-Angulo A.M., Hennessy B., Green M., et al. Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy and Long-Term Survival in Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023;41:1809–1815. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.02572. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blows F.M., Driver K.E., Schmidt M.K., Broeks A., van Leeuwen F.E., Wesseling J., Cheang M.C., Gelmon K., Nielsen T.O., Blomqvist C., et al. Subtyping of breast cancer by immunohistochemistry to investigate a relationship between subtype and short and long term survival: A collaborative analysis of data for 10,159 cases from 12 studies. PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000279. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

