Using Deauville Scoring to Guide Consolidative Radiotherapy in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 39409931
- PMCID: PMC11475697
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16193311
Using Deauville Scoring to Guide Consolidative Radiotherapy in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
Background: The most common aggressive lymphoma in adults is diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Consolidative radiotherapy (RT) is often administered to DLBCL patients but guidelines remain unclear, which could lead to unnecessary RT. We aimed to evaluate the value of end-of-treatment PET-CT scans, interpreted using the Deauville score (DV), to guide the utilization of consolidative RT, which may help spare low-risk DLBCL patients from unnecessary RT.
Methods: We included all DLBCL patients diagnosed between 2010 and 2022 at the National Cancer Centre Singapore with DV measured at the end of the first-line chemoimmunotherapy. The outcome measure was time-to-progression (TTP). The predictive value of DV for RT was assessed based on the interaction effect between the receipt of RT and DV in Cox regression models.
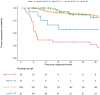
Results: The data of 349 patients were analyzed. The median follow-up time was 38.1 months (interquartile range 34.0-42.3 months). RT was associated with a significant improvement in TTP amongst the DV4-5 patients (HR 0.33; 95%CI 0.13-0.88; p = 0.027) but not the DV1-3 patients (HR 0.85; 95%CI 0.40-1.81; p = 0.671) (interaction's p = 0.133). Multivariable analysis reported that RT was again significantly associated with improved TTP among the DV4-5 patients (adjusted HR 0.29; 95%CI 0.10-0.80; p = 0.017) but not the DV1-3 group (HR 0.86; 95%CI 0.40-1.86; p = 0.707) (interaction's p = 0.087).
Conclusion: Our results suggests that DLBCL patients with end-of-treatment PET-CT DV1-3 may not need consolidative RT. Longer follow-up and prospective randomized trials are still necessary to investigate long-term outcomes.
Keywords: DLBCL; PET-CT; consolidative treatment; de-escalation; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Al Armashi A.R., Al Zubaidi A., Mahmood O., Thierheimer M., Alkrekshi A., Abdulhaq H. Trends in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Mortality in the United States: A Comprehensive Review from 2000 to 2020. Blood. 2023;142((Suppl. S1)):1765. doi: 10.1182/blood-2023-180270. - DOI
-
- Chua B.J.G., Low C.E., Yau C.E., Tan Y.H., Chiang J., Chang E.W.Y., Chan J.Y., Poon E.Y.L., Somasundaram N., Rashid M.F.B.H., et al. Recent updates on central nervous system prophylaxis in patients with high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024;13:1. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00467-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Crump M., Neelapu S.S., Farooq U., Van Den Neste E., Kuruvilla J., Westin J., Link B.K., Hay A., Cerhan J.R., Zhu L., et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood. 2017;130:1800–1808. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-03-769620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ip A., Mutebi A., Wang T., Jun M., Kalsekar A., Navarro F.R., Wang A., Kamalakar R., Sacchi M., Elliott B. Treatment Outcomes with Standard of Care in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Real-World Data Analysis. Adv. Ther. 2024;41:1226–1244. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02775-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources