Bilateral Trade Welfare Impacts of India's Export Ban of Non-Basmati Rice Using the Global Partial Equilibrium Simulation Model (GSIM)
- PMID: 39410159
- PMCID: PMC11482592
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13193124
Bilateral Trade Welfare Impacts of India's Export Ban of Non-Basmati Rice Using the Global Partial Equilibrium Simulation Model (GSIM)
Abstract
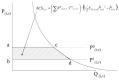
India, the world's leading rice exporter, banned the export of non-Basmati white rice, accounting for 25% of its total exports (or 10% of the global rice trade). The ban aims to ensure availability to domestic Indian consumers and reduce domestic market prices, impacting global rice market accessibility, consumers, and producers across twelve regions. The study utilized the global simulation model (GSIM) to analyze the effects of trade restrictions on industries. The model uses national product differentiation to assess trade policy changes at global, regional, or national scales. It examined importer and exporter effects on trade values, tariff revenues, exporter surplus, and importer surplus. It found that India's Voluntary Export Restraint (VER) ban on non-Basmati rice resulted in a higher local price and a negative global net welfare impact of USD 1.7 billion. The losses decreased to USD 1.4 billion when importing countries responded by reducing rice import tariffs by 25% and USD 1.1 billion when importing countries reduced tariffs by 75%. Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, North Africa, and the Gulf Cooperation Council regions were most affected. The study also found minimal impact on consumer surplus in India due to inelastic rice demand.
Keywords: food trade; partial equilibrium global simulation model (GSIM); rice; trade barriers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Mohidem N.A., Hashim N., Shamsudin R., Che Man H. Rice for Food Security: Revisiting Its Production, Diversity, Rice Milling Process and Nutrient Content. Agriculture. 2022;12:741. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12060741. - DOI
-
- USDA World Rice Production 2021/2022. [(accessed on 3 September 2023)];2022 Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/pub-details/?pubid=105472.
-
- Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development . OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2022–2031. Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development; Paris, France: 2018. OECD Agriculture Statistics (Database) - DOI
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) [(accessed on 20 October 2023)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/markets-and-trade/commodities/rice/fao-rice-price-up...
-
- How Export Restrictions Are Impacting Global Food Prices. [(accessed on 6 July 2023)]. Available online: https://blogs.worldbank.org/psd/how-export-restrictions-are-impacting-gl....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

