Pectin Microwave Assisted Extraction from Pumpkin Peels: Process Optimization and Chemical-Physical and Rheological Characterization
- PMID: 39410192
- PMCID: PMC11475461
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13193157
Pectin Microwave Assisted Extraction from Pumpkin Peels: Process Optimization and Chemical-Physical and Rheological Characterization
Abstract
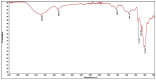
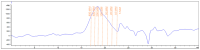
Recently, pectin, a versatile polysaccharide with different industrial applications, has gained significant attention as an eco-friendly and functional ingredient. This study investigates pumpkin peels (Cucurbita maxima L., Mantua variety) as a novel source of pectin, using a microwave-assisted extraction method with citric acid-acidified water as solvent. The extraction conditions were optimized using a Design of Experiments approach, considering the solvent-to-solid ratio (SSR), pH, temperature, and extraction time. The optimized conditions (94.8 °C, 5 min, pH 1.5, and 46 mL/g SSR) resulted in a pectin yield of 18.05%. A comprehensive characterization of the extracted pectin was performed, including FT-IR spectroscopy, DSC, TGA, rheological properties, and techno-functional assessments such as water holding capacity and fat binding capacity. The results indicated a high degree of esterification (56.19 ± 0.87%), classifying the pumpkin peels (PP) extract as a high methoxyl pectin. PP pectin demonstrated potential as a stabilizer and emulsifying agent, although its high methoxyl content limits its use as a carrier for targeted bioactive delivery. The findings support the viability of using agricultural by-products to obtain valuable polysaccharides, contributing to waste valorization and sustainable industrial practices.
Keywords: agrifood waste; by-products; emulsifier agent; high methoxyl pectin; pumpkin peels pectin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the study’s design; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 of 9 March 2012 Laying Down Specifications for Food Additives Listed in Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council Text with EEA Relevance. [(accessed on 5 May 2024)]. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32012R0231.
-
- Rodríguez Robledo V., Castro Vázquez L.I. Pectin—Extraction, purification, characterization and applications. In Pectin Extraction, Purification, Characterization and Applications. In: Masuelli M., editor. 1st ed. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2020. pp. 65–83.
-
- Dib T., Pan H., Chen S. Recent advances in pectin-based nanoencapsulation for enhancing the bioavailability of bioactive compounds: Curcumin oral bioavailability. Food Rev. Int. 2022;39:1–19. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2021.2012796. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

