Evaluation of C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 5 (CCR5) as a Sample Adequacy Control in HPV Molecular Diagnostics
- PMID: 39410598
- PMCID: PMC11482552
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14192194
Evaluation of C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 5 (CCR5) as a Sample Adequacy Control in HPV Molecular Diagnostics
Abstract
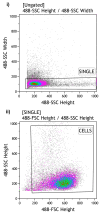
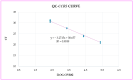
Background: Reliable Human Papillomavirus (HPV) testing and genotyping are essential for quality assurance in HPV-based primary screening, disease management and for monitoring the impact of HPV vaccination. The clinical validation of HPV molecular diagnostic assays has significantly contributed to these objectives; however, little emphasis has been placed on assuring sample quality. This study aimed to evaluate the accuracy of sample cellularity assessment using the C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 5 (CCR5) gene target as a marker of sample adequacy in molecular diagnostics. Methods: Jurkat cell line samples were counted using both a Thoma cell-counting chamber and Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS). Jurkat cell line samples at three different concentrations were subsequently evaluated using the OncoPredict HPV Quality Control (QC) real-time PCR assay, employing CCR5 for molecular cellularity quantification. Results: The cellularity values obtained were comparable across the three different methods for all dilutions of the cell line tested. Conclusions: The results obtained from this study show that CCR5 represents a promising molecular marker for the accurate quantification of sample cellularity, confirming its use as a reliable sample adequacy control, thus reducing the risk of "false-negative" results.
Keywords: C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 5 (CCR5); Human Papillomavirus (HPV); OncoPredict HPV Quality Control (QC) assay; sample adequacy control (SAC).
Conflict of interest statement
CEC received research funding and consumables to support research from the following commercial entities in the last 3 years: BD, Seegene, Copan, Novosanis and Hiantis; CEC is a minority shareholder of Hiantis. SRL., R.C.N., M.M., C.G., S.D.M., B.T., M.D.A., M.S. and C.B have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) to Screen for Cervical Pre-Cancer Lesions and Prevent Cervical Cancer. [(accessed on 30 January 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240045248.
-
- Rijkaart D.C., Berkhof J., Rozendaal L., van Kemenade F.J., Bulkmans N.W.J., Heideman D.A.M., Kenter G.G., Cuzick J., Snijders P.J.F., Meijer C.J.L.M. Human Papillomavirus Testing for the Detection of High-Grade Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Cancer: Final Results of the POBASCAM Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:78–88. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70296-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ronco G., Dillner J., Elfström K.M., Tunesi S., Snijders P.J.F., Arbyn M., Kitchener H., Segnan N., Gilham C., Giorgi-Rossi P., et al. Efficacy of HPV-Based Screening for Prevention of Invasive Cervical Cancer: Follow-up of Four European Randomised Controlled Trials. Lancet. 2014;383:524–532. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62218-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

