Active role of the immune system in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
- PMID: 39411101
- PMCID: PMC11479709
- DOI: 10.1093/gastro/goae089
Active role of the immune system in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Abstract
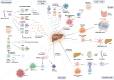
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, recently renamed metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), is a complex multifactorial disease that progresses from steatohepatitis (MASH) to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Recent research has revealed that crosstalk between innate immune cells and hepatic parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells is involved in the pathogenesis of liver disease in MASLD/MASH. Of particular importance, novel inflammatory mechanisms, including macrophage diversity, neutrophil NETosis, B-cell biology, auto-reactive T cells, unconventional T cells, and dendritic cell-T cell interactions, are considered key drivers for disease progression. These mechanisms and factors are potential targets for the therapeutic intervention of MASLD/MASH. In this review, we focus on recent discoveries related to liver inflammation and discuss the role of innate immune cell subsets in MASLD/MASH.
Keywords: MASH; MASLD; inflammatory cytokine; innate immunity; liver fibrosis.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press and Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University.
Conflict of interest statement
T.K. and S.Y. received lecture fees from Gilead Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M. et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;15:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Lazarus JV, Mark HE, Anstee QM. et al. NAFLD Consensus Consortium. Advancing the global public health agenda for NAFLD: a consensus statement. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;19:60–78. - PubMed
-
- Tsochatzis EA. Natural history of NAFLD: knowns and unknowns. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;19:151–2. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

