Age-related hearing loss in older adults: etiology and rehabilitation strategies
- PMID: 39411148
- PMCID: PMC11473498
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1428564
Age-related hearing loss in older adults: etiology and rehabilitation strategies
Abstract
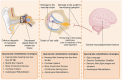
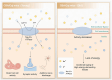
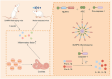
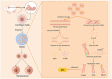
Age-related hearing loss (ARHL) is a prevalent sensory organ disorder among elderly individuals that significantly impacts their cognitive function, psychological well-being, and ability to perform activities of daily living. As the population ages, the number of ARHL patients is increasing. However, the Audiological rehabilitation (AR) status of patients is not promising. In recent years, there has been an increasing focus on the health and rehabilitation of elderly individuals, and significant progress has been made in researching various age-related disorders. However, a unified definition of ARHL in terms of etiology and rehabilitation treatment is still lacking. This study aims to provide a reference for future research on ARHL and the development of AR strategies by reviewing the classification, etiology, and rehabilitation of ARHL.
Keywords: age-related hearing loss; elderly; presbycusis; rehabilitation; review.
Copyright © 2024 Zheng, Xu, Li, Wang, Zhang and Jing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-related hearing loss: quality of care for quality of life.Gerontologist. 2012 Apr;52(2):265-71. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnr159. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Gerontologist. 2012. PMID: 22383543 Review.
-
Age-related hearing loss and tinnitus, dementia risk, and auditory amplification outcomes.Ageing Res Rev. 2019 Dec;56:100963. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2019.100963. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Ageing Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 31557539 Review.
-
The Age-Related Central Auditory Processing Disorder: Silent Impairment of the Cognitive Ear.Front Neurosci. 2019 Jun 14;13:619. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00619. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31258467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Age-Related Hearing Loss on Working Memory among Older Individuals: An Event-Related Potential Study.Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2024 Mar 12;14(1):1-13. doi: 10.1159/000538109. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2024. PMID: 38601851 Free PMC article.
-
Slowing the progression of age-related hearing loss: Rationale and study design of the ASPIRIN in HEARING, retinal vessels imaging and neurocognition in older generations (ASPREE-HEARING) trial.Contemp Clin Trials. 2016 Jan;46:60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2015.11.014. Epub 2015 Nov 28. Contemp Clin Trials. 2016. PMID: 26611434 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Association Between Unaided Speech Perception in Noise and Hearing Aid Use Mediated by Perceived Benefit.Audiol Res. 2025 May 1;15(3):50. doi: 10.3390/audiolres15030050. Audiol Res. 2025. PMID: 40407664 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Aging Potential of Avocado Oil via Its Antioxidant Effects.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 12;18(2):246. doi: 10.3390/ph18020246. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andries E., Bosmans J., Engelborghs S., Cras P., Vanderveken O. M., Lammers M. J. W., et al. . (2023). Evaluation of cognitive functioning before and after Cochlear implantation in adults aged 55 years and older at risk for mild cognitive impairment. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 149, 310–316. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2022.5046 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anzivino R., Conti G., di Nardo W., Fetoni A. R., Picciotti P. M., Marra C., et al. . (2019). Prospective evaluation of cognitive functions after rehabilitation with Cochlear implant or hearing aids: preliminary results of a multicentric study on elderly patients. Am. J. Audiol. 28, 762–774. doi: 10.1044/2019_AJA-HEAL18-18-0176, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

