Diagnosis and Management of Retrograde Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39411246
- PMCID: PMC11474230
- DOI: 10.1002/oto2.70014
Diagnosis and Management of Retrograde Cricopharyngeal Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Objective: Retrograde cricopharyngeal dysfunction (R-CPD) is a syndrome with rapidly increasing awareness since being first described in March 2019. As such, few cases of R-CPD are currently reported in the literature. The goal of this study is to provide a comprehensive systematic review of the available literature on R-CPD, including patient characteristics, diagnosis, and management.
Data sources: PubMed, Scopus, EMBASE.
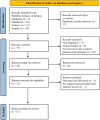
Review methods: A systematic review of the available English literature was conducted using the data sources PubMed, Scopus, and EMBASE. Studies with original data of patients experiencing classic symptoms of R-CPD were included. Independent abstract screening followed by full-text screening was performed to assess study eligibility. Data extraction of patient demographics, symptoms, treatment, and follow-up were subsequently performed.
Results: Common presentations of R-CPD include abelchia (100%), abdominal bloating (83%), and gurgling noises (75%). 554 (86.9%) patients had improved symptoms after initial treatment with BTX. The most common initial dose was 50 units in 204 (37.3%) patients. Subsequent BTX injections resolved symptoms in 40 (80%) patients. Six patients ultimately received CP myotomy for recurrent symptoms, resulting in long-term resolution in 4 (67%) patients.
Conclusion: R-CPD is a newly recognized syndrome with effective treatment options including botulinum toxin injections and cricopharyngeal myotomy, where appropriate. Diagnostic modalities including esophageal manometry may aid in the initial work up of R-CPD, however further studies are required to assess its diagnostic utility.
Keywords: abelchia; botulinum toxin; cricopharyngeal myotomy; retrograde cricopharyngeal dysfunction.
© 2024 The Author(s). OTO Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- r/noburp . Accessed July 8, 2024. https://www.reddit.com/r/noburp/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

