Clinical Insights on Caloric Restriction Mimetics for Mitigating Brain Aging and Related Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 39412683
- PMCID: PMC11485046
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-024-01493-2
Clinical Insights on Caloric Restriction Mimetics for Mitigating Brain Aging and Related Neurodegeneration
Abstract
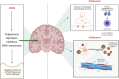
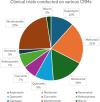
Aging, an inevitable physiological process leading to a progressive decline in bodily functions, has been an abundantly researched domain with studies attempting to slow it down and reduce its debilitating effects. Investigations into the cellular and molecular pathways associated with aging have allowed the formulation of therapeutic strategies. Of these, caloric restriction (CR) has been implicated for its role in promoting healthy aging by modulating key molecular targets like Insulin/IGF-1, mTOR, and sirtuins. However, CR requires dedication and commitment to a strict regimen which poses a difficulty in maintaining consistency. To maneuver around cumbersome diets, Caloric Restriction Mimetics (CRMs) have emerged as promising alternatives by mimicking the beneficial effects of CR. This review elucidates the molecular foundations enabling CRMs like rapamycin, metformin, resveratrol, spermidine, and many more to function as suitable anti-aging molecules. Moreover, it explores clinical trials (retrieved from the clinicaltrials.gov database) aimed at demonstrating the efficacy of CRMs as effective candidates against age-related neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Aging; Alzheimer’s disease; CR-mimetics; Caloric restriction; Clinical trials; Parkinson’s disease.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed T, Gilani AH, Abdollahi M et al (2015) Berberine and neurodegeneration: a review of literature. Pharmacol Rep 67:970–979. 10.1016/j.pharep.2015.03.002 - PubMed
-
- Amanzadeh E, Esmaeili A, Rahgozar S, Nourbakhshnia M (2019) Application of quercetin in neurological disorders: from nutrition to nanomedicine. Rev Neurosci 30:555–572. 10.1515/revneuro-2018-0080 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

