Spatial transcriptomic analysis of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the human brain
- PMID: 39414359
- PMCID: PMC11495544
- DOI: 10.1503/jpn.240026
Spatial transcriptomic analysis of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the human brain
Abstract
Background: Adult hippocampal neurogenesis has been extensively characterized in rodent models, but its existence in humans remains controversial. We sought to assess the phenomenon in postmortem human hippocampal samples by combining spatial transcriptomics and multiplexed fluorescent in situ hybridization.
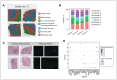
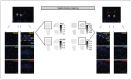
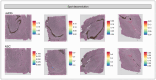
Methods: We computationally examined the spatial expression of various canonical neurogenesis markers in postmortem dentate gyrus (DG) sections from young and middle-aged sudden-death males. We conducted in situ assessment of markers expressed in neural stem cells, proliferative cells, and immature granule neurons in postmortem DG sections from infant, adolescent, and middle-aged males.
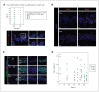
Results: We examined frozen DG tissue from infant (n = 1, age 2 yr), adolescent (n = 1, age 16 yr), young adult (n = 2, mean age 23.5 yr), and middle-aged (n = 2, mean age 42.5 yr) males, and frozen-fixed DG tissue from middle-aged males (n = 6, mean age 43.5 yr). We detected very few cells expressing neural stem cell and proliferative markers in the human DG from childhood to middle age. However, at all ages, we observed a substantial number of DG cells expressing the immature neuronal marker DCX. Most DCX + cells displayed an inhibitory phenotype, while the remainder were non-committed or excitatory in nature.
Limitations: The study was limited by small sample sizes and included samples only from males.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate very low levels of hippocampal neurogenesis throughout life and the existence of a local reserve of plasticity in the adult human hippocampus. Overall, our study provides important insight into the distribution and phenotype of cells expressing neurogenesis markers in the adult human hippocampus.
© 2024 CMA Impact Inc. or its licensors.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:: None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Björk-Eriksson T, et al. . Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 1998;4:1313–7. - PubMed
-
- Flor-Garcia M, Terreros-Roncal J, Moreno-Jimenez EP, et al. . Unraveling human adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nat Protoc 2020; 15:668–93. - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Jimenez EP, Flor-Garcia M, Terreros-Roncal J, et al. . Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med 2019;25:554–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

