Arterial stiffness measured by pulse wave velocity correlated with cognitive decline in hypertensive individuals: a systematic review
- PMID: 39415095
- PMCID: PMC11481605
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-024-03905-8
Arterial stiffness measured by pulse wave velocity correlated with cognitive decline in hypertensive individuals: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Arterial stiffness is a degenerative modification in the arterial wall that significantly affects normal aging. Arterial hypertension is a major risk factor for cerebrovascular impairment. Pulse wave velocity (PWV) is an established gold standard for measuring arterial stiffness. Studies demonstrated that individuals with elevated blood pressure (BP) and PWV are more likely to experience worse cognitive decline compared to those with either condition alone. The aim of this review is to explore the clinical importance of arterial stiffness for cognitive function in older adults with hypertension.
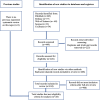
Methods: The systematic review was reported following the PRISMA 2020 guidelines and Cochrane protocol and was registered in NIHR PROSPERO. PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CINAHL, and Cochrane databases were searched for relevant publications up to December 2022. Articles were filtered by age and type of study and only those including a sample size of at least 500 individuals were selected. Screening of abstracts and full-text review of selected articles were carried out through Covidence.
Results: The full-text review included a total of 434 articles. Twenty-eight prospective studies have met the inclusion criteria. Selected studies used PWV as the main measurement of stiffness: 24 used carotid-femoral, 2 used brachial-ankle, 1 used aortic PWV, and 11 compared different measures. Studies demonstrated a strong association between increased BP and PWV with brain damage and cognitive deterioration among older adults. One study did not find an interaction with hypertension, while another study found that PWV but not BP was associated with cognitive decline. Few studies showed that the association between stiffness and cognitive outcomes was not significant after adjustment for BP. Several authors suggested that cognitive decline induced by stiff vasculature and hypertension benefited from antihypertensive therapy.
Conclusion: The results of this review demonstrated that arterial hypertension is an important factor linking arterial stiffness to cognitive health in older individuals. BP plays a crucial role in brain integrity, whereas PWV was shown to be a strong measure associated with cognitive decline. Together, they can lead to disabling cognitive outcomes. Early screening of stiffness, BP control, and compliance with treatment are essential for cerebrovascular disease prevention.
Trial registration: NIHR PROSPERO registry ID: CRD42022379887 .
Keywords: Aging; Arterial hypertension; Arterial stiffness; Cognitive decline; Pulse wave velocity.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
-
- Comfort A. Feasibility in age research. Nature. 1968;217(5126):320–2. - PubMed
-
- Boytsov SA, Samorodskaya IV. [Cardiovascular disease and cognitive impairment]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2022;122(7):7–13. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA, Butler J, Dracup K, Ezekowitz MD, Finkelstein EA, Hong Y, Johnston SC, Khera A, Lloyd-Jones DM, Nelson SA, Nichol G, Orenstein D, Wilson PWF, Woo YJ. Forecasting the future of Cardiovascular Disease in the United States. Circulation. 2011;123(8):933–44. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redón J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013;31(7):1281–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous