Pro-inflammatory cytokines increase temporarily after adjuvant treatment for breast cancer in postmenopausal women: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 39415181
- PMCID: PMC11481761
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-024-01898-3
Pro-inflammatory cytokines increase temporarily after adjuvant treatment for breast cancer in postmenopausal women: a longitudinal study
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer patients have an increased risk of cardiometabolic disease and for many patients, adjuvant therapy causes an altered lipid profile, insulin resistance and inflammation. Previous follow-up studies are inconclusive regarding the duration of therapy-induced inflammation. We examined the acute and persistent changes of adjuvant chemotherapy on inflammatory and metabolic health markers in breast cancer patients.
Methods: Plasma levels of IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IFN-γ, TNF-α, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and metabolic health parameters were analyzed before, shortly after and every six months up to two years after adjuvant chemotherapy treatment in 51 postmenopausal early breast cancer (EBC) patients, as well as in 41 healthy age- and BMI-matched controls. A target-specific multiplex assay was applied for cytokine measurements.
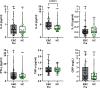
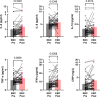
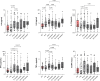
Results: Before initiation of adjuvant therapy, plasma IL-8 levels were higher in EBC patients (31%, p = 0.0001). Also, a larger proportion of the patients had a hsCRP level above 2 mg/L (41%) compared to the controls (17%, Χ2 = 5.15, p = 0.023). Plasma levels of all five cytokines, but not hsCRP, were significantly increased after compared to before adjuvant chemotherapy (15-48% increase; all p ≤ 0.05). Already six months after ending chemotherapy treatment, all plasma cytokine levels were significantly reduced and close to pre-chemotherapy levels. Adjuvant chemotherapy caused a worsened lipid profile (increased triglycerides, lower HDL levels), insulin resistance and increased plasma insulin levels that remained high during the first year after chemotherapy.
Conclusion: Postmenopausal women with EBC have temporarily increased plasma levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines after adjuvant chemotherapy. Although transient, the therapy-induced increase in plasma cytokine levels, together with dyslipidemia and insulin resistance, may contribute to cardiometabolic risk in breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy.
Trial registration: The clinical trial (registration number NCT03784651) was registered on www.
Clinicaltrials: gov on 24 December 2018.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cardiometabolic; Chemotherapy; Cytokines; Inflammation; Metabolism; Side effects.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL, Siegel RL. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:363–85. - PubMed
-
- Trédan O, Bajard A, Meunier A, et al. Body weight change in women receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: a French prospective study. Clin Nutr. 2010;29:187–91. - PubMed
-
- Buch-Larsen K, Lund-Jacobsen T, Andersson M, Schwarz P. Weight change in post-menopausal women with breast cancer during chemotherapy-perspectives on nutrition, activity and bone metabolism: an interim analysis of a 5-year prospective cohort. Nutrients. 2021;13(8):2902. 10.3390/nu13082902. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

